Molecular mechanism of modulating miR482b level in tomato with botrytis cinerea infection
- PMID: 34706648
- PMCID: PMC8555085
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-021-03203-2
Molecular mechanism of modulating miR482b level in tomato with botrytis cinerea infection
Abstract
Background: Plant miRNAs are involved in the response to biotic and abiotic stresses by altering their expression levels, and they play an important role in the regulation of plant resistance to stress. However, the molecular mechanism that regulates the expression levels of miRNAs in plants with biotic and abiotic stress still needs to be explored. Previously, we found that the expression of the miR482 family was changed in tomato infected by Botrytis cinerea. In this study, we investigated and uncovered the mechanism underlying the response of miR482 to B. cinerea infection in tomato.
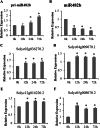
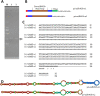
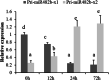
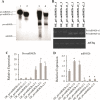
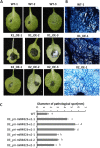
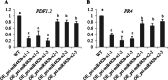
Results: First, RT-qPCR was employed to detect the expression patterns of miR482b in tomato infected by B. cinerea, and results showed that miR482b primary transcripts (pri-miR482b) were up-regulated in B. cinerea-infected leaves, but the mature miR482b was down-regulated. Subsequently, we used rapid amplification cDNA end method to amplify the full-length of pri-miR482b. Result showed that the pri-miR482b had two isoforms, with the longer one (consisting 300 bp) having an extra fragment of 53 bp in the 3'-end compared with the shorter one. In vitro Dicer assay indicated that the longer isoform pri-miR482b-x1 had higher efficiency in the post-transcriptional splicing of miRNA than the shorter isoform pri-miR482b-x2. In addition, the transcription level of mature miR482b was much higher in transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing pri-miR482b-x1 than that in OE pri-miR482b-x2 Arabidopsis. These results confirmed that this extra 53 bp in pri-miR482b-x1 might play a key role in the miR482b biogenesis of post-transcription processing.
Conclusions: Extra 53 bp in pri-miR482b-x1 enhanced miR482b biogenesis, which elevated the transcription level of miR482b. This study clarified the response of miR482 to B. cinerea infection in tomato, thereby helping us further understand the molecular mechanisms that regulate the expression levels of other miRNAs.
Keywords: Botrytis cinerea; pathogen response; posttranscriptional processing; pri-miR482b isoforms; sly-miR482b.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miR319c acts as a positive regulator of tomato against Botrytis cinerea infection by targeting TCP29.Plant Sci. 2020 Nov;300:110610. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2020.110610. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 33180702
-
Characterization of miRNAs associated with Botrytis cinerea infection of tomato leaves.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Jan 16;15:1. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0410-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25592487 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of the expression of WRKY75 transcription factor in response to biotic and abiotic stresses in Solanaceae plants.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Jan;37(1):167-176. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2219-8. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29079899
-
Determination of histone epigenetic marks in Arabidopsis and tomato genes in the early response to Botrytis cinerea.Plant Cell Rep. 2018 Jan;37(1):153-166. doi: 10.1007/s00299-017-2218-9. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29119291
-
Mechanisms and strategies of plant defense against Botrytis cinerea.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017 Mar;37(2):262-274. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2016.1271767. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28056558 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptome and 16S rRNA analysis revealed the response of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) to Rhabdovirus infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 7;13:973422. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.973422. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275642 Free PMC article.
-
New insight into the molecular mechanism of miR482/2118 during plant resistance to pathogens.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Oct 28;13:1026762. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1026762. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36388487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tae-miR397 Negatively Regulates Wheat Resistance to Blumeria graminis.Plants (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;12(17):3096. doi: 10.3390/plants12173096. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37687344 Free PMC article.
-
MIR390 Is Involved in Regulating Anthracnose Resistance in Apple.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 29;11(23):3299. doi: 10.3390/plants11233299. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501336 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic weapons of plants against fungal pathogens.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Mar 6;24(1):175. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04829-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38443788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
- LY21C140004 and LY18C150010/This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, and the 521 Talent Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University.
- LY21C140004 and LY18C150010/This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, and the 521 Talent Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University.
- LY21C140004 and LY18C150010/This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, and the 521 Talent Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University.
- LY21C140004 and LY18C150010/This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, and the 521 Talent Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University.
- LY21C140004 and LY18C150010/This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, and the 521 Talent Foundation of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

