SquiggleNet: real-time, direct classification of nanopore signals
- PMID: 34706748
- PMCID: PMC8548853
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-021-02511-y
SquiggleNet: real-time, direct classification of nanopore signals
Abstract
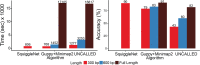
We present SquiggleNet, the first deep-learning model that can classify nanopore reads directly from their electrical signals. SquiggleNet operates faster than DNA passes through the pore, allowing real-time classification and read ejection. Using 1 s of sequencing data, the classifier achieves significantly higher accuracy than base calling followed by sequence alignment. Our approach is also faster and requires an order of magnitude less memory than alignment-based approaches. SquiggleNet distinguished human from bacterial DNA with over 90% accuracy, generalized to unseen bacterial species in a human respiratory meta genome sample, and accurately classified sequences containing human long interspersed repeat elements.
Keywords: Deep learning; Oxford Nanopore; Raw signal; Read-until; Real-time.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Oxford Nanopore: Minion. https://nanoporetech.com/products/minion. Accessed 10 Sept 2019.
-
- Gnirke A, Melnikov A, Maguire J, Rogov P, LeProust EM, Brockman W, Fennell T, Giannoukos G, Fisher S, Russ C, Gabriel S, Jaffe DB, Lander ES, Nusbaum C. Solution hybrid selection with ultra-long oligonucleotides for massively parallel targeted sequencing. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27(2):182–89. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

