Assessment of the efficiency of synergistic photocatalysis on penicillin G biodegradation by whole cell Paracoccus sp
- PMID: 34706751
- PMCID: PMC8554860
- DOI: 10.1186/s13036-021-00275-4
Assessment of the efficiency of synergistic photocatalysis on penicillin G biodegradation by whole cell Paracoccus sp
Abstract
Background: The Paracoccus sp. strain isolated from sludge was identified and evaluated for catalytic activity in the degradation of penicillin G.
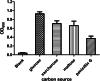
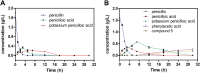
Results: High degradation efficiency and synergistic catalytic effects of the whole cell and visible light without additional catalysts were observed. The key factors influencing the degradation and kinetics of penicillin G were investigated. The results showed the phenylacetic acid, which was produced during penicillin G biodegradation, exhibited stronger inhibiting effects on KDSPL-02. However, this effect was reduced by visible light irradiation without any additional photocatalyst; furthermore, the rate of penicillin G biodegradation was accelerated, reaching a 100% rate in 12 h at a penicillin G concentration of 1.2 g/L. Four key intermediates produced during penicillin G degradation were isolated and identified by LC-MS, 1H NMR, and 13C NMR. Enzymes involved in the PAA pathway were proposed from a genomic analysis of KDSPL-02.
Conclusions: These results provide a new method for bio-degrading of penicillin or other antibiotic pollutants using photoaccelerating biocatalysts with greater efficiency and more environmentally friendly conditions.
Keywords: Biodegradation; Paracoccus sp. strain; Penicillin G; Synergistic catalysis; Visible light.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Not applicable.
Figures




References
-
- von Dach E, Albrich WC, Brunel AS, Prendki V, Cuvelier C, Flury D, et al. Effect of C-reactive protein-guided antibiotic treatment duration, 7-day treatment, or 14-day treatment on 30-day clinical failure rate in patients with uncomplicated gram-negative bacteremia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020;323(21):2160–2169. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.6348. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Liu H, Dai X, Cai C, Wang J, Wang M, et al. Impact of application of heat-activated persulfate oxidation treated erythromycin fermentation residue as a soil amendment: soil chemical properties and antibiotic resistance. Sci Total Environ. 2020;736:139668. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139668. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

