Comparison of the chemical constituents and anti-Alzheimer's disease effects of Uncaria rhynchophylla and Uncaria tomentosa
- PMID: 34706756
- PMCID: PMC8555092
- DOI: 10.1186/s13020-021-00514-2
Comparison of the chemical constituents and anti-Alzheimer's disease effects of Uncaria rhynchophylla and Uncaria tomentosa
Abstract
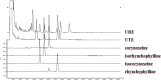
Background: Uncaria tomentosa, which has similar chemical constituents with Uncaria rhynchophylla, has been reported to alleviate cognitive impairments in Alzheimer's disease (AD) animal models. This study aimed to compare the chemical constituents and anti-AD effect of the ethanol extracts of U. tomentosa (UTE) and U. rhynchophylla (URE).
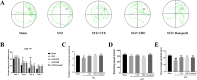
Methods: The high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was used to compare the chemical constituents of UTE and URE. Streptozotocin (STZ) was intracerebroventricularly (ICV) injected into adult male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats to establish AD model. UTE (400 mg/kg) or URE (400 mg/kg) was administrated intragastrically once daily to the rats for 6 consecutive weeks. Morris water maze (MWM) test was conducted to assess the neurological functions in the STZ-induced AD rats. The brain tissues of the rats were harvested for further biochemical assay.
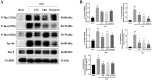
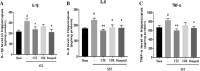
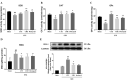
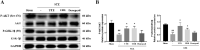
Results: The MWM test results showed both UTE and URE could significantly improve the learning and memory impairments induced by STZ in rats. Both UTE and URE could significantly inhibit the hyperphosphorylation of tau protein, reduce the elevated levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α), enhance activities of antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT and GPx) and increase the protein expression of HO-1. In addition, UTE could decrease the malondialdehyde (MDA) level. Furthermore, both UTE and URE significantly enhanced Akt activation, down regulated the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK-3β), and induced the nuclear translocation of Nrf2 in the STZ-induced AD rats.
Conclusions: UTE and URE contained similar chemical constituents. We found for the first time that both of them could ameliorate cognitive deficits in the STZ-induced AD rats. The underlying molecular mechanism involve suppression of tau hyperphosphorylation, anti-oxidant and anti-neuroinflammation via modulating Akt (Ser473)/GSK3β (Ser9)-mediated Nrf2 activation. These findings amply implicate that both of UTE and URE are worthy of being developed clinically into pharmaceutical treatment for AD.
Keywords: Akt/GSK3β/Nrf2 pathway; Alzheimer’s disease; Rats; Streptozotocin; Uncaria rhynchophylla; Uncaria tomentosa.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Patchouli alcohol ameliorates the learning and memory impairments in an animal model of Alzheimer's disease via modulating SIRT1.Phytomedicine. 2022 Nov;106:154441. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154441. Epub 2022 Sep 6. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 36108371
-
Sulforaphene Ameliorates Neuroinflammation and Hyperphosphorylated Tau Protein via Regulating the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Pathway in Experimental Models of Alzheimer's Disease.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Sep 10;2020:4754195. doi: 10.1155/2020/4754195. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32963694 Free PMC article.
-
Uncaria rhynchophylla Ameliorates Parkinson's Disease by Inhibiting HSP90 Expression: Insights from Quantitative Proteomics.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(4):1453-1464. doi: 10.1159/000490837. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29940559
-
Uncaria rhynchophylla and its Major Constituents on Central Nervous System: A Review on Their Pharmacological Actions.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(4):346-357. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190704092841. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31272356 Review.
-
The beneficial pharmacological effects of Uncaria rhynchophylla in neurodegenerative diseases: focus on alkaloids.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 31;15:1436481. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1436481. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39170707 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-inflammatory and/or immunomodulatory activities of Uncaria tomentosa (cat's claw) extracts: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo studies.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 31;15:1378408. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1378408. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38881881 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Analysis of Metabolites from Peruvian Native Plants as Potential Therapeutics against Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2022 Jan 28;27(3):918. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030918. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164183 Free PMC article.
-
Patchouli alcohol attenuates the cognitive deficits in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease via modulating neuropathology and gut microbiota through suppressing C/EBPβ/AEP pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jan 30;20(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02704-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36717922 Free PMC article.
-
Uncaria tomentosa as a Promising Natural Source of Molecules with Multiple Activities: Review of Its Ethnomedicinal Uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacology.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 15;26(14):6758. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146758. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40725012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uncaria tomentosa extract exerts antimicrobial activity against boar seminal bacteria and influences sperm resilience under different conditions.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Mar 21;12:1558650. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1558650. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40191089 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death; 2020. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed 20 Mar 2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

