Rhabdomyolysis Caused by Gefitinib Overdose
- PMID: 34707044
- PMCID: PMC9177374
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.8168-21
Rhabdomyolysis Caused by Gefitinib Overdose
Abstract
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) are common therapeutic agents for EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. There has been no report of rhabdomyolysis caused by an overdose of EGFR-TKIs. We herein review the existing literature on the subject and report a rare case of rhabdomyolysis due to an overdose of gefitinib, an EGFR-TKI.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; overdose; rhabdomyolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
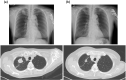


References
-
- Akechi T, Okamura H, Nishiwaki Y, Uchitomi Y. Psychiatric disorders and associated and predictive factors in patients with unresectable nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: a longitudinal study. Cancer 92: 2609-2622, 2001. - PubMed
-
- Koršić M, Muršić D, Badovinac S, et al. . Erlotinib-related rhabdomyolysis: the role of pharmacogenetics and drug-drug interaction. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 76: 1317-1319, 2015. - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa R, Yoneyama R, Miyajima K, et al. . 2 cases that afatinib was considered as a cover suspicion medicine for rhabdomyolysis. Jpn J Lung Cancer 56: 663, 2016.
-
- Temel JS, Greer JA, Muzikansky A, et al. . Early palliative care for patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 363: 733-742, 2010. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

