ITSN1: a novel candidate gene involved in autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder spectrum
- PMID: 34707297
- PMCID: PMC8738743
- DOI: 10.1038/s41431-021-00985-9
ITSN1: a novel candidate gene involved in autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder spectrum
Abstract
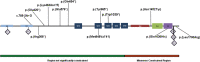
ITSN1 plays an important role in brain development. Recent studies in large cohorts of subjects with neurodevelopmental disorders have identified de novo variants in ITSN1 gene thereby suggesting that this gene is involved in the development of such disorders. The aim of this study is to provide further proof of such a link. We performed trio exome sequencing in a patient presenting autism, intellectual disability, and severe behavioral difficulties. Additional affected patients with a neurodevelopmental disorder harboring a heterozygous variant in ITSN1 (NM_003024.2) were collected through a worldwide collaboration. All patients underwent detailed phenotypic and genetic assessment and data was collected and shared by healthcare givers. We identified ten novel patients from eight families with heterozygous truncating or missense variants in ITSN1 gene. In addition, four previously published patients from large meta-analysis studies were included. In total, 7/14 patients presented a de novo variant in ITSN1. All patients showed neurodevelopmental disorders from autism spectrum disorders (90%), intellectual disability (86%), and epilepsy (30%). We demonstrated that truncating variants are in the first half of ITSN1 whereas missense variants are clustered in C-terminal region. We suggest ITSN1 gene is involved in development of an autism spectrum disorder with variable additional neurodevelopmental deficiency, thus confirming the hypothesis that ITSN1 is important for brain development.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to European Society of Human Genetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Patel DR, Apple R, Kanungo S, Akkal A. Intellectual disability: definitions, evaluation and principles of treatment, Pediatric Med. 2018;1. 10.21037/pm.2018.12.02.
-
- Stojanovic JR, Miletic A, Peterlin B, Maver A, Mijovic M, Borlja N, et al. Diagnostic and clinical utility of clinical exome sequencing in children with moderate and severe global developmental delay/intellectual disability. J Child Neurol. 2020;35:116–31. doi: 10.1177/0883073819879835. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases