Paclitaxel: Application in Modern Oncology and Nanomedicine-Based Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 34707776
- PMCID: PMC8545549
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3687700
Paclitaxel: Application in Modern Oncology and Nanomedicine-Based Cancer Therapy
Abstract
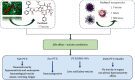
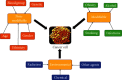
Paclitaxel is a broad-spectrum anticancer compound, which was derived mainly from a medicinal plant, in particular, from the bark of the yew tree Taxus brevifolia Nutt. It is a representative of a class of diterpene taxanes, which are nowadays used as the most common chemotherapeutic agent against many forms of cancer. It possesses scientifically proven anticancer activity against, e.g., ovarian, lung, and breast cancers. The application of this compound is difficult because of limited solubility, recrystalization upon dilution, and cosolvent-induced toxicity. In these cases, nanotechnology and nanoparticles provide certain advantages such as increased drug half-life, lowered toxicity, and specific and selective delivery over free drugs. Nanodrugs possess the capability to buildup in the tissue which might be linked to enhanced permeability and retention as well as enhanced antitumour influence possessing minimal toxicity in normal tissues. This article presents information about paclitaxel, its chemical structure, formulations, mechanism of action, and toxicity. Attention is drawn on nanotechnology, the usefulness of nanoparticles containing paclitaxel, its opportunities, and also future perspective. This review article is aimed at summarizing the current state of continuous pharmaceutical development and employment of nanotechnology in the enhancement of the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic features of paclitaxel as a chemotherapeutic agent.
Copyright © 2021 Javad Sharifi-Rad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no declarations of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Choudhury H., Maheshwari R., Pandey M., Takede M., Gorain B., Tekade R. Advanced nanoscale carrier-based approaches to overcome biopharmaceutical issues associated with anticancer drug ‘Etoposide’. Materials Science and Engineering: C . 2020;106, article 110275 doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2019.110275. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Perreira-Silva M., Alvarez-Lorenzo C., Concheiro A., Santos A., Veiga F., Figueiras A. Nanomedicine in osteosarcoma therapy: micelleplexes for delivery of nucleic acids and drugs toward osteosarcoma-targeted therapies. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics . 2020;148:88–106. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.10.013. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Feng B., Niu Z., Hou B., Zhou L., Li Y., Yu H. Enhancing triple negative breast cancer immunotherapy by ICG-templated self-assembly of paclitaxel nanoparticles. Advanced Functional Materials . 2019;30(6):1–13.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

