Liver abnormalities in pulmonary arterial hypertension
- PMID: 34707859
- PMCID: PMC8544777
- DOI: 10.1177/20458940211054304
Liver abnormalities in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Abstract
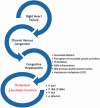
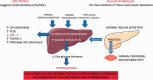
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a cardiopulmonary disease with high mortality. In recent years, it has been recognized that PAH is a multi-organ system disease, involving the systemic circulation, kidneys, skeletal muscles, and the central nervous system, among others. Right heart failure produces congestive hepatopathy, a disease state that has direct consequences on liver biochemistry, histology, and systemic glucose and lipid metabolism. This article aims to summarize the consequences of congestive hepatopathy with an emphasis on liver biochemistry, histology, and PAH-targeted therapy. Furthermore, PAH-specific changes in glucose and lipid metabolism will be discussed.
Keywords: lipid metabolism; liver; pulmonary arterial hypertension; venous congestion.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Rosenkranz S, Howard LS, Gomberg-Maitland M, et al.. Systemic consequences of pulmonary hypertension and right-sided heart failure. Circulation 2020; 141: 678–693. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources