Biochemical and transcriptomic analyses reveal that critical genes involved in pigment biosynthesis influence leaf color changes in a new sweet osmanthus cultivar 'Qiannan Guifei'
- PMID: 34707941
- PMCID: PMC8504463
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.12265
Biochemical and transcriptomic analyses reveal that critical genes involved in pigment biosynthesis influence leaf color changes in a new sweet osmanthus cultivar 'Qiannan Guifei'
Abstract
Background: Osmanthus fragrans (Oleaceae) is one of the most important ornamental plant species in China. Many cultivars with different leaf color phenotypes and good ornamental value have recently been developed. For example, a new cultivar 'Qiannan Guifei', presents a rich variety of leaf colors, which change from red to yellow-green and ultimately to green as leaves develop, making this cultivar valuable for landscaping. However, the biochemical characteristics and molecular mechanisms underlying leaf color changes of these phenotypes have not been elucidated. It has been hypothesized that the biosynthesis of different pigments in O. fragrans might change during leaf coloration. Here, we analyzed transcriptional changes in genes involved in chlorophyll (Chl), flavonoid, and carotenoid metabolic pathways and identified candidate genes responsible for leaf coloration in the new cultivar 'Qiannan Guifei'.
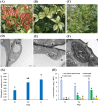
Methods: Leaf samples were collected from 'Qiannan Guifei' plants at the red (R), yellow-green (YG) and green (G) leaf stages. We compared the different-colored leaves via leaf pigment concentrations, chloroplast ultrastructure, and transcriptomic data. We further analyzed differentially expressed genes (DEGs) involved in the Chl, flavonoid, and carotenoid metabolic pathways. In addition, we used qRT-PCR to validate expression patterns of the DEGs at the three stages.
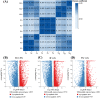
Results: We found that, compared with those at the G stage, chloroplasts at the R and YG stages were less abundant and presented abnormal morphologies. Pigment analyses revealed that the leaves had higher flavonoid and anthocyanin levels at the R stage but lower Chl and carotenoid concentrations. Similarly, Chl and carotenoid concentrations were lower at the YG stage than at the G stage. By using transcriptomic sequencing, we further identified 61 DEGs involved in the three pigment metabolic pathways. Among these DEGs, seven structural genes (OfCHS, OfCHI, OfF3H, OfDFR, OfANS, OfUGT andOf3AT) involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway were expressed at the highest level at the R stage, thereby increasing the biosynthesis of flavonoids, especially anthocyanins. Six putativeOfMYB genes, including three flavonoid-related activators and three repressors, were also highly expressed at the R stage, suggesting that they might coordinately regulate the accumulation of flavonoids, including anthocyanins. Additionally, expressions of the Chl biosynthesis-related genes OfHEMA, OfCHLG and OfCAO and the carotenoid biosynthesis-related genes OfHYB and OfZEP were upregulated from the R stage to the G stage, which increased the accumulation of Chl and carotenoids throughout leaf development. In summary, we screened the candidate genes responsible for the leaf color changes of 'Qiannan Guifei', improved current understanding of the regulatory mechanisms underlying leaf coloration and provided potential targets for future leaf color improvement in O. fragrans.
Keywords: Anthocyanin; Carotenoid; Chlorophyll; Flavonoid; Leaf color; OfMYB genes; Osmanthus fragrans ‘Qiannan Guifei’.
©2021 Cui et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mechanisms for leaf color changes in Osmanthus fragrans 'Ziyan Gongzhu' using physiology, transcriptomics and metabolomics.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Sep 27;23(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04457-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37752431 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and Comparative Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Key Genes Involved in Major Metabolic Regulation Related to Colored Leaf Formation in Osmanthus fragrans 'Yinbi Shuanghui' during Development.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 4;10(4):549. doi: 10.3390/biom10040549. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32260448 Free PMC article.
-
SWATH-MS based proteomics reveals the role of photosynthesis related proteins and secondary metabolic pathways in the colored leaves of sweet olive (Osmanthus fragrans).BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 1;25(1):1026. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10867-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39487388 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Metabolites of Osmanthus fragrans: Metabolism and Medicinal Value.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 18;13:922204. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.922204. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35924042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosynthesis and Extraction of Chlorophyll, Carotenoids, Anthocyanins, and Betalaine In Vivo and In Vitro.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 23;46(9):10662-10676. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090633. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329984 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albert NW, Arathoon S, Collette VE, Schwinn KE, Jameson PE, Lewis DH, Zhang HB, Davies KM. Activation of anthocyanin synthesis in Cymbidium orchids: variability between known regulators. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture. 2010;100:355–360. doi: 10.1007/s11240-009-9649-0. - DOI
-
- Barry CS, Aldridge GM, Herzog G, Ma Q, McQuinn RP, Hirschberg J, Giovannoni JJ. Altered chloroplast development and delayed fruit ripening caused by mutations in a zinc metalloprotease at the lutescent2 locus of tomato. Plant Physiology. 2012;159(3):1086–1098. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.197483. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

