Interactions Among lncRNA/circRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Musculoskeletal Degenerative Diseases
- PMID: 34708047
- PMCID: PMC8542847
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.753931
Interactions Among lncRNA/circRNA, miRNA, and mRNA in Musculoskeletal Degenerative Diseases
Abstract
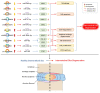
Musculoskeletal degenerative diseases (MSDDs) are pathological conditions that affect muscle, bone, cartilage, joint and connective tissue, leading to physical and functional impairments in patients, mainly consist of osteoarthritis (OA), intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD), rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs (circRNAs) are novel regulators of gene expression that play an important role in biological regulation, involving in chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis, extracellular matrix degradation and peripheral blood mononuclear cell inflammation. Research on MSDD pathogenesis, especially on RA and AS, is still in its infancy and major knowledge gaps remain to be filled. The effects of lncRNA/circRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis on MSDD progression help us to fully understand their contribution to the dynamic cellular processes, provide the potential OA, IDD, RA and AS therapeutic strategies. Further studies are needed to explore the mutual regulatory mechanisms between lncRNA/circRNA regulation and effective therapeutic interventions in the pathology of MSDD.
Keywords: age-related disease; aging; circRNA; degenerative musculoskeletal disorders; lncRNA; miRNA; non-coding RNAs.
Copyright © 2021 Zheng, Song, Guo, Su, Chen, Yang, Chen and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

