Severity of diabetic retinopathy and its relationship with age at onset of diabetes mellitus in India: A multicentric study
- PMID: 34708783
- PMCID: PMC8725142
- DOI: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_1459_21
Severity of diabetic retinopathy and its relationship with age at onset of diabetes mellitus in India: A multicentric study
Abstract
Purpose: To present clinical profile and risk factors of sight-threatening diabetic retinopathy (STDR) among people with age of onset of diabetes (AOD) <25 versus ≥25 years.
Methods: A retrospective chart analysis of consecutive patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR) n = 654) treated at 14 eye care centers across India between 2018 and 2019 was performed. Patients were divided into two groups, Group 1: AOD <25 years and Group 2: AOD ≥25 years. DR and diabetic macular edema (DME) were classified using the International Clinical Classification of DR severity scale. STDR included severe nonproliferative DR (NPDR), proliferative DR (PDR), and moderate to severe DME. A multilevel mixed-effects model was used for comparison between two groups: 1) Patients with DR and AOD <25 years and 2) Patients with DR and AOD ≥25 years. Bivariate and multivariate regression analyses were used to evaluate risk factors between the two groups.
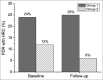
Results: A total of 654 patients were included, 161 (307 eyes) in AOD <25 and 493 (927 eyes) in AOD >25 group. There was a higher prevalence of PDR with high-risk characteristics in AOD <25 group (24% vs. 12%) at baseline and 12-month follow-up (25% vs. 6%); P < 0.001. Systolic hypertension and poor glycemic control were risk factors in both groups, with no difference in these modifiable risk factors between groups.
Conclusion: People with youth-onset DM are likely to present with severer form of STDR despite similar modifiable risk factors. Therefore, strict control of systolic blood pressure, glycemic status, and regular screening for DR are recommended to reduce the risk of STDR irrespective of the age of onset of diabetes.
Keywords: Age of onset of diabetes; diabetes mellitus; diabetic retinopathy; severity; sight-threatening.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: Predictors of development and progression of diabetic retinopathy: A precis.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov;69(11):3261-3262. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_2213_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34708784 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Praveen PA, Madhu SV, Viswanathan M, Das S, Kakati S, Shah N, et al. Demographic and clinical profile of youth onset diabetes patients in India—Results from the baseline data of a clinic based registry of people with diabetes in India with young age at onset—[YDR-02] Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22:15–21. - PubMed
-
- Amutha A, Ranjit U, Anjana RM, Shanthi R CS, Rajalakshmi R, Venkatesan U, et al. Clinical profile and incidence of microvascular complications of childhood and adolescent onset type 1 and type 2 diabetes seen at a tertiary diabetes center in India. Pediatr Diabetes. 2021;22:67–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

