Sevoflurane protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via microrna-30c-5p modulating homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 1
- PMID: 34709114
- PMCID: PMC8810137
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1999551
Sevoflurane protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via microrna-30c-5p modulating homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 1
Abstract
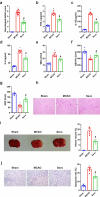
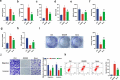
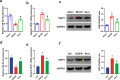
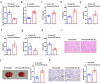
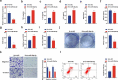
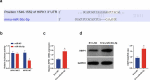
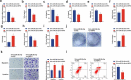
Sevoflurane (SEV) has been reported to be an effective neuroprotective agent for cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (CIRI). However, the precise molecular mechanisms of Sev preconditioning in CIRI remain largely unknown. Therefore, CIRI model was established via middle cerebral artery occlusion method. SEV was applied before modeling. after successful modeling, lentivirus was injected into the lateral ventricle of the brain. Neurological impairment score was performed in each group, and histopathologic condition, infarct volume, apoptosis, inflammation, oxidative stress, microRNA (miR)-30 c-5p and homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 1 (HIPK1) were detected. Mouse hippocampal neuronal cell line HT22 cells were pretreated with SEV, and the in vitro model was stimulated via oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation. The corresponding plasmids were transfected, and the cell growth was detected, including inflammation and oxidative stress, etc. The targeting of miR-30 c-5p with HIPK1 was examined. The results clarified that reduced miR-30 c-5p and elevated HIPK1 were manifested in CIRI. SEV could improve CIRI and modulate the miR-30 c-5p-HIPK1 axis in vitro and in vivo, and miR-30 c-5p could target HIPK1. Depressed miR-30 c-5p could eliminate the protection of SEV in vitro and in vivo. Repression of HIPK1 reversed the effect of reduced miR-30 c-5p on CIRI. Therefore, it is concluded that SEV is available to depress CIRI via targeting HIPK1 through upregulated miR-30 c-5p.
Keywords: Cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury; Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 1; MicroRNA-30c-5p; Sevoflurane.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sevoflurane prevents miR-181a-induced cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury.Chem Biol Interact. 2019 Aug 1;308:332-338. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2019.06.008. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Chem Biol Interact. 2019. PMID: 31170386
-
Sevoflurane regulates DICER1 expression by targeting miR-192-5p to protect cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.Gen Physiol Biophys. 2024 Nov;43(6):511-523. doi: 10.4149/gpb_2024032. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39584296
-
MiR-30c-5p-Targeted Regulation of GNAI2 Improves Neural Function Injury and Inflammation in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Aug;196(8):5235-5248. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04802-5. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38153649
-
Flurbiprofen axetil protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulating miR-30c-5p and SOX9.Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022 Feb;99(2):197-205. doi: 10.1111/cbdd.13973. Epub 2021 Oct 21. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2022. PMID: 34651418
-
Long noncoding RNA SOX2OT silencing alleviates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via miR-135a-5p-mediated NR3C2 inhibition.Brain Res Bull. 2021 Aug;173:193-202. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2021.05.018. Epub 2021 May 20. Brain Res Bull. 2021. PMID: 34022287
Cited by
-
Dual effects of GABA A R agonist anesthetics in neurodevelopment and vulnerable brains: From neurotoxic to therapeutic effects.Neural Regen Res. 2026 Jan 1;21(1):81-95. doi: 10.4103/NRR.NRR-D-24-00828. Epub 2024 Dec 7. Neural Regen Res. 2026. PMID: 39665822 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Role of MicroRNA-30c in Neurological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 20;24(1):37. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010037. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting anesthesia-induced preconditioning for neuroprotection in the aging brain: a narrative review.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025 Jun;78(3):187-198. doi: 10.4097/kja.25073. Epub 2025 Mar 20. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2025. PMID: 40112780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of lncRNA SNHG16 in oxidative stress and inflammation in oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced SK-N-SH cells.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):5021-5034. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2026861. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35170375 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hayashida K, Sano M, Ohsawa I, et al. Inhalation of hydrogen gas reduces infarct size in the rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem biophys res commun. 2008;373:30–35. - PubMed
-
- Kersten J, Schmeling T, Hettrick D, et al. Mechanism of myocardial protection by isoflurane. role of adenosine triphosphate-regulated potassium (KATP) channels. Anesthesiology. 1996;85(4):794–807. discussion 727a. - PubMed
-
- Kersten J, Schmeling T, Pagel P, et al. Isoflurane mimics ischemic preconditioning via activation of K(ATP) channels: reduction of myocardial infarct size with an acute memory phase. Anesthesiology. 1997;87:361–370. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
