Avatrombopag: A Review in Thrombocytopenia
- PMID: 34709601
- PMCID: PMC8610948
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-021-01613-y
Avatrombopag: A Review in Thrombocytopenia
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Avatrombopag: A Review in Thrombocytopenia.Drugs. 2021 Dec;81(18):2169. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01651-6. Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34843098 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
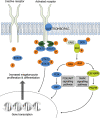
Avatrombopag (Doptelet®) is an orally administered second generation thrombopoietin receptor agonist (TPO-RA) approved for the treatment of primary chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) in adult patients who are refractory or have an unsatisfactory response to other treatments, as well as for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic liver disease (CLD) scheduled to undergo an invasive procedure. In phase III studies, avatrombopag was associated with a significantly greater platelet response than placebo in patients with chronic ITP, and was superior to placebo in reducing the requirement for platelet transfusion or rescue procedures for bleeding caused by surgery in patients with CLD with a platelet count < 50 × 109/L at baseline. Longer term data indicate that avatrombopag is associated with high durable response rates in ITP and may have corticosteroid-sparing effects. The drug was generally well tolerated in both indications. Avatrombopag thus represents a convenient and effective second-line treatment for patients with chronic ITP and can prevent bleeding events in patients with CLD scheduled to undergo a procedure, offering a useful alternative to other available treatments in both indications.
Plain language summary
Avatrombopag (Doptelet®) is an orally administered drug that mimics the natural compound (thrombopoietin) responsible for stimulating the production of platelets, an essential component of the clotting process that prevents excessive bleeding. Several conditions can cause reduced platelet levels (thrombocytopenia) to the point that intervention is needed to prevent excessive blood loss. Avatrombopag is approved for the treatment of primary chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) and to prevent bleeding caused by surgery in patients with low platelet levels caused by chronic liver disease (CLD). Clinical trials in patients with ITP show that avatrombopag quickly increases platelet levels and that this increase is maintained in the longer term in many patients. Similarly, clinical trials in patients with low platelet levels because of CLD showed that giving avatrombopag prior to surgery reduced the need for platelet transfusions or rescue procedures for bleeding. Avatrombopag is thus a convenient and effective treatment for patients with chronic ITP and can prevent bleeding events in patients with CLD scheduled to undergo a procedure. In both indications avatrombopag offers a useful alternative to other available treatments.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Markham is a salaried employee of Adis International Ltd/Springer Nature, and declares no relevant conflicts of interest. All authors contributed to the review and are responsible for the article content.
References
-
- Kuter D. MSD manual: professional version; overview of platelet disorders. 2020. https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/hematology-and-oncology/thromboc.... Accessed 17 Sep 2021.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources