Halogen Transfer to Carbon Radicals by High-Valent Iron Chloride and Iron Fluoride Corroles
- PMID: 34709780
- PMCID: PMC9082684
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.1c02666
Halogen Transfer to Carbon Radicals by High-Valent Iron Chloride and Iron Fluoride Corroles
Abstract
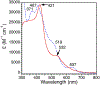
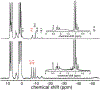
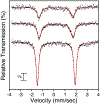
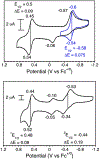
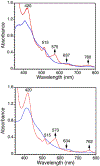
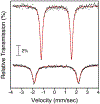
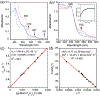
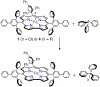
High-valent iron halide corroles were examined to determine their reactivity with carbon radicals and their ability to undergo radical rebound-like processes. Beginning with Fe(Cl)(ttppc) (1) (ttppc = 5,10,15-tris(2,4,6-triphenylphenyl)corrolato3-), the new iron corroles Fe(OTf)(ttppc) (2), Fe(OTf)(ttppc)(AgOTf) (3), and Fe(F)(ttppc) (4) were synthesized. Complexes 3 and 4 are the first iron triflate and iron fluoride corroles to be structurally characterized by single crystal X-ray diffraction. The structure of 3 reveals an AgI-pyrrole (η2-π) interaction. The Fe(Cl)(ttppc) and Fe(F)(ttppc) complexes undergo halogen transfer to triarylmethyl radicals, and kinetic analysis of the reaction between (p-OMe-C6H4)3C• and 1 gave k = 1.34(3) × 103 M-1 s-1 at 23 °C and 2.2(2) M-1 s-1 at -60 °C, ΔH⧧ = +9.8(3) kcal mol-1, and ΔS⧧ = -14(1) cal mol-1 K-1 through an Eyring analysis. Complex 4 is significantly more reactive, giving k = 1.16(6) × 105 M-1 s-1 at 23 °C. The data point to a concerted mechanism and show the trend X = F- > Cl- > OH- for Fe(X)(ttppc). This study provides mechanistic insights into halogen rebound for an iron porphyrinoid complex.
Figures
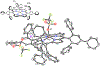

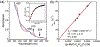
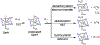
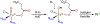
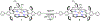
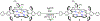
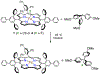
References
-
- Rittle J; Green MT, Cytochrome P450 Compound I: Capture, Characterization, and C-H Bond Activation Kinetics. Science, 2010, 330, 933. - PubMed
-
- Denisov IG; Makris TM; Sligar SG; Schlichting I, Structure and Chemistry of Cytochrome P450. Chem. Rev, 2005, 105, 2253. - PubMed
-
- Makris TM; Koenig K. v.; Schlichting I; Sligar SG, The status of high-valent metal oxo complexes in the P450 cytochromes. J. Inorg. Biochem, 2006, 100, 507. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

