Minimal Residual Disease Dynamics after Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab Treatment: Extended Off-Treatment Follow-up From the Randomized CLL14 Study
- PMID: 34709929
- PMCID: PMC8678026
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.21.01181
Minimal Residual Disease Dynamics after Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab Treatment: Extended Off-Treatment Follow-up From the Randomized CLL14 Study
Abstract
Purpose: The CLL14 study has established one-year fixed-duration treatment of venetoclax and obinutuzumab (Ven-Obi) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. With all patients off treatment for at least three years, we report a detailed analysis of minimal residual disease (MRD) kinetics and long-term outcome of patients treated in the CLL14 study.
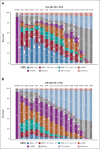
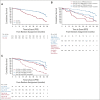
Patients and methods: Patients were randomly assigned to receive six cycles of obinutuzumab with 12 cycles of venetoclax or 12 cycles of chlorambucil (Clb-Obi). Progression-free survival (PFS) was the primary end point. Key secondary end points included rates of undetectable MRD and overall survival. To analyze MRD kinetics, a population-based growth model with nonlinear mixed effects approach was developed.
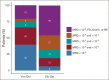
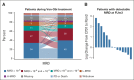
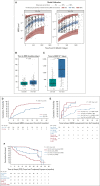
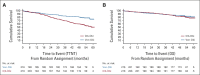
Results: Of 432 patients, 216 were assigned to Ven-Obi and 216 to Clb-Obi. Three months after treatment completion, 40% of patients in the Ven-Obi arm (7% in the Clb-Obi arm) had undetectable MRD levels < 10-6 by next-generation sequencing in peripheral blood. Median MRD doubling time was longer after Ven-Obi than Clb-Obi therapy (median 80 v 69 days). At a median follow-up of 52.4 months, a sustained significant PFS improvement was observed in the Ven-Obi arm compared with Clb-Obi (median not reached v 36.4 months; hazard ratio 0.33; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.45; P < .0001). The estimated 4-year PFS rate was 74.0% in the Ven-Obi and 35.4% in the Clb-Obi arm. No difference in overall survival was observed (hazard ratio 0.85; 95% CI, 0.54 to 1.35; P = .49). No new safety signals occurred.
Conclusion: Appearance of MRD after Ven-Obi is significantly slower than that after Clb-Obi with more effective MRD reduction. These findings translate into a superior long-term efficacy with the majority of Ven-Obi-treated patients remaining in remission.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02242942.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Thompson M, Brander D, Nabhan C, et al. : Minimal residual disease in chronic lymphocytic leukemia in the era of novel agents: A review. JAMA Oncol 4:394-400, 2018 - PubMed
-
- Al-Sawaf O, Zhang C, Tandon M, et al. : Venetoclax plus obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab for previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL14): Follow-up results from a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 21:1188-1200, 2020 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

