CBX2 Induces Glioma Cell Proliferation and Invasion Through the Akt/PI3K Pathway
- PMID: 34709960
- PMCID: PMC8558802
- DOI: 10.1177/15330338211045831
CBX2 Induces Glioma Cell Proliferation and Invasion Through the Akt/PI3K Pathway
Abstract
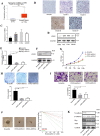
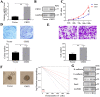
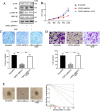
Glioma is the most common primary intracranial tumor. Abnormal expression of CBX2 (ChromoBox2) is associated with tumorigenesis and tumor development. TCGA data in UALCAN showed that CBX2 was overexpressed in glioma tissue. To confirm the role of CBX2 in glioma, we regulated the level of CBX2 and conducted colony formation, Transwell, and CCK-8 assays to verify the effect of CBX2. The results showed that CBX2 knockdown reduced glioma cell proliferation and invasion and that the cells were less tumorigenic. CBX2 overexpression induced glioma cell proliferation and invasion and glioma stem cell self-renewal. The animal experiments showed that CBX2 knockdown inhibited glioma growth and improved survival time. CBX2 knockdown inhibited activation of the Akt/PI3K pathway. epidermal growth factor rescued the effects of CBX2. CBX2 could induce the growth and invasion of glioma cells via the Akt/PI3K pathway.
Keywords: Akt; CBX2; PI3K; glioma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- McNeill KA. Epidemiology of brain tumors. Neurol Clin. 2016;34(4):981‐998. - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Reardon DA. Neuro-oncology in 2015: progress in glioma diagnosis, classification and treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2016;12(2):69‐70. - PubMed
-
- Soomro SH, Ting LR, Qing YY, Ren M. Molecular biology of glioblastoma: classification and mutational locations. J Pak Med Assoc. 2017;67(9):1410‐1414. - PubMed
-
- Gil J, Bernard D, Martínez D, Beach D. Polycomb CBX7 has a unifying role in cellular lifespan. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(1):67‐72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

