Impact of persistent D-dimer elevation following recovery from COVID-19
- PMID: 34710097
- PMCID: PMC8553152
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0258351
Impact of persistent D-dimer elevation following recovery from COVID-19
Abstract
Background: Elevated D-dimer is known as predictor for severity of SARS-CoV2-infection. Increased D-dimer is associated with thromboembolic complications, but it is also a direct consequence of the acute lung injury seen in COVID-19 pneumonia.
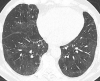
Objectives: To evaluate the rate of persistent elevated D-dimer and its association with thromboembolic complications and persistent ground glass opacities (GGO) after recovery from COVID-19.
Methods: In this post hoc analysis of a prospective multicenter trial, patients underwent blood sampling, measurement of diffusion capacity, blood gas analysis, and multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) scan following COVID-19. In case of increased D-dimer (>0,5 μg/ml), an additional contrast medium-enhanced CT was performed in absence of contraindications. Results were compared between patients with persistent D-dimer elevation and patients with normal D-dimer level.
Results: 129 patients (median age 48.8 years; range 19-91 years) underwent D-Dimer assessment after a median (IQR) of 94 days (64-130) following COVID-19. D-dimer elevation was found in 15% (19/129) and was significantly more common in patients who had experienced a severe SARS-CoV2 infection that had required hospitalisation compared to patients with mild disease (p = 0.049). Contrast-medium CT (n = 15) revealed an acute pulmonary embolism in one patient and CTEPH in another patient. A significant lower mean pO2 (p = 0.015) and AaDO2 (p = 0.043) were observed in patients with persistent D-Dimer elevation, but the rate of GGO were similar in both patient groups (p = 0.33).
Conclusion: In 15% of the patients recovered from COVID-19, persistent D-dimer elevation was observed after a median of 3 months following COVID-19. These patients had experienced a more severe COVID and still presented more frequently a lower mean pO2 and AaDO2.
Conflict of interest statement
NO authors have competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shah S, Shah K, Patel SB, Patel FS, Osman M, Velagapudi P, et al. Elevated D-Dimer Levels Are Associated With Increased Risk of Mortality in Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiol Rev. 2020. Nov/Dec;28(6):295–302. doi: 10.1097/CRD.0000000000000330 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous