Lower-limb kinematics and kinetics during continuously varying human locomotion
- PMID: 34711856
- PMCID: PMC8553836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41597-021-01057-9
Lower-limb kinematics and kinetics during continuously varying human locomotion
Abstract
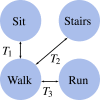
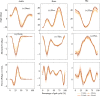
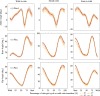
Human locomotion involves continuously variable activities including walking, running, and stair climbing over a range of speeds and inclinations as well as sit-stand, walk-run, and walk-stairs transitions. Understanding the kinematics and kinetics of the lower limbs during continuously varying locomotion is fundamental to developing robotic prostheses and exoskeletons that assist in community ambulation. However, available datasets on human locomotion neglect transitions between activities and/or continuous variations in speed and inclination during these activities. This data paper reports a new dataset that includes the lower-limb kinematics and kinetics of ten able-bodied participants walking at multiple inclines (±0°; 5° and 10°) and speeds (0.8 m/s; 1 m/s; 1.2 m/s), running at multiple speeds (1.8 m/s; 2 m/s; 2.2 m/s and 2.4 m/s), walking and running with constant acceleration (±0.2; 0.5), and stair ascent/descent with multiple stair inclines (20°; 25°; 30° and 35°). This dataset also includes sit-stand transitions, walk-run transitions, and walk-stairs transitions. Data were recorded by a Vicon motion capture system and, for applicable tasks, a Bertec instrumented treadmill.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Azocar, A. F., Mooney, L. M., Hargrove, L. J. & Rouse, E. J. Design and characterization of an open-source robotic leg prosthesis. In 2018 7th IEEE Int. Conf. Biomed. Robot. Biomechatronics, 111–118, 10.1109/BIOROB.2018.8488057 (2018).
-
- Lenzi T, et al. Design, development, and testing of a lightweight hybrid robotic knee prosthesis. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2018;37:953–976. doi: 10.1177/0278364918785993. - DOI
-
- Lawson BE, et al. A robotic leg prosthesis: Design, control, and implementation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Mag. 2014;21:70–81. doi: 10.1109/MRA.2014.2360303. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

