Association Between Apelin and Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With High Risk of Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 34712712
- PMCID: PMC8545982
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.742601
Association Between Apelin and Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With High Risk of Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
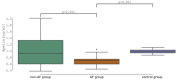
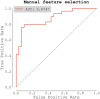
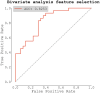
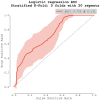
Background: Atrial fibrillation (AF) is associated with high risk of stroke preventable by timely initiation of anticoagulation. Currently available screening tools based on ECG are not optimal due to inconvenience and high costs. Aim of this study was to study the diagnostic value of apelin for AF in patients with high risk of stroke. Methods: We designed a multicenter, matched-cohort study. The population consisted of three study groups: a healthy control group (34 patients) and two matched groups of 60 patients with high risk of stroke (AF and non-AF group). Apelin levels were examined from peripheral blood. Results: Apelin was significantly lower in AF group compared to non-AF group (0.694 ± 0.148 vs. 0.975 ± 0.458 ng/ml, p = 0.001) and control group (0.982 ± 0.060 ng/ml, p < 0.001), respectively. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis of apelin as a predictor of AF scored area under the curve (AUC) of 0.658. Apelin's concentration of 0.969 [ng/ml] had sensitivity = 0.966 and specificity = 0.467. Logistic regression based on manual feature selection showed that only apelin and NT-proBNP were independent predictors of AF. Logistic regression based on selection from bivariate analysis showed that only apelin was an independent predictor of AF. A logistic regression model using repeated stratified K-Fold cross-validation strategy scored an AUC of 0.725 ± 0.131. Conclusions: Our results suggest that apelin might be used to rule out AF in patients with high risk of stroke.
Keywords: apelin; atrial fibrillation; biomarker; electrical atrial remodeling; ischemic stroke.
Copyright © 2021 Bohm, Snopek, Tothova, Bezak, Jajcay, Vachalcova, Uher, Kurecko, Kissova, Danova, Olejnik, Michalek, Hlavata, Petrikova, Mojto, Kyselovic and Farsky.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. . 2020 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European association for cardio-thoracic surgery (EACTS): the task force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European society of cardiology (ESC) developed with the special contribution of the European heart rhythm association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur Heart J. (2021) 42:373–498. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vermond RA, Geelhoed B, Verweij N, Tieleman RG, Van der Harst P, Hillege HL, et al. . Incidence of atrial fibrillation and relationship with cardiovascular events, heart failure, and mortality: a community-based study from the Netherlands. J Am Coll Cardiol. (2015) 66:1000–7. 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.06.1314 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

