Non-invasive Technology Advances in Cancer-A Review of the Advances in the Liquid Biopsy for Endometrial and Ovarian Cancers
- PMID: 34713045
- PMCID: PMC8521848
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.573010
Non-invasive Technology Advances in Cancer-A Review of the Advances in the Liquid Biopsy for Endometrial and Ovarian Cancers
Abstract
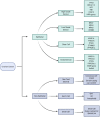
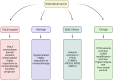
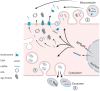
Improving cancer survival rates globally requires improvements in disease detection and monitoring, with the aim of improving early diagnosis and prediction of disease relapse. Traditional means of detecting and monitoring cancers rely largely on imaging and, where possible, blood-based protein biomarkers, many of which are non-specific. Treatments are being improved by identification of inherited and acquired genomic aberrations in tumors, some of which can be targeted by newly developed therapeutic interventions. Treatment of gynecological malignancy is progressively moving toward personalized therapy, as exemplified by application of PARP-inhibition for patients with BRCA-deficient tubo-ovarian cancers, or checkpoint inhibition in patients with mismatch repair-deficient disease. However, the more recent discovery of a group of biomarkers described under the umbrella term of "liquid biopsy" promises significant improvement in our ability to detect and monitor cancers. The term "liquid biopsy" is used to describe an array of tumor-derived material found in blood plasma and other bodily fluids such as ascites, pleural fluid, saliva, and urine. It includes circulating tumors cells (CTCs), circulating nucleic acids including DNA, messenger RNA and micro RNAs, and extracellular vesicles (EVs). In this review, we discuss recent advancements in liquid biopsy for biomarker detection to help in diagnosis, prognosis, and planning of treatment of ovarian and endometrial cancer.
Keywords: DNA; biomarker; circulating tumor (ctDNA); circulating tumor cell (CTC); microRNA.
Copyright © 2020 Openshaw and McVeigh.
Conflict of interest statement
TM has received speaking honoraria from Roche, Novartis, Astra Zeneca, MSD, and Merck. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lodish H, Berk A, Zipursky SL. Proto-oncogenes and tumor suppressor genes. In: Freeman WH. editor. Molecular Cell Biology. New York, NY: W. H. Freeman and Company; (2000).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

