The Upcoming Role for Nursing and Assistive Robotics: Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
- PMID: 34713058
- PMCID: PMC8521866
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2020.585656
The Upcoming Role for Nursing and Assistive Robotics: Opportunities and Challenges Ahead
Abstract
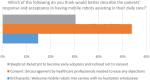
As an integral part of patient care, nursing is required to constantly adapt to changes in the healthcare system, as well as the wider financial and societal environment. Among the key factors driving these changes is the aging of population. Combined with an existing shortage of nursing and caregiving professionals, accommodating for the patients and elderly needs within hospitals, elderly-care facilities and at a home setting, becomes a societal challenge. Amongst the technological solutions that have evolved in response to these developments, nursing and assistive robotics claim a pivotal role. The objective of the present study is to provide an overview of today's landscape in nursing and assistive robotics, highlighting the benefits associated with adopting such solutions in standard clinical practice. At the same time, to identify existing challenges and limitations that essentially outline the area's future directions. Beyond technological innovation, the manuscript also investigates the end-users' angle, being a crucial parameter in the success of robotics solutions operating within a healthcare environment. In this direction, the results of a survey designed to capture the nursing professionals' perspective toward more informed robotics design and development are presented.
Keywords: connected health; eHealth; healthcare robotics; nursing robots; physically-assistive robots; robotics; socially-assistive robots.
Copyright © 2020 Christoforou, Avgousti, Ramdani, Novales and Panayides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Robotics in Nursing: A Scoping Review.J Nurs Scholarsh. 2018 Nov;50(6):590-600. doi: 10.1111/jnu.12424. Epub 2018 Sep 27. J Nurs Scholarsh. 2018. PMID: 30260093
-
Socially Assistive Robots (SAR) in In-Patient Care for the Elderly.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2019;260:178-185. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2019. PMID: 31118335
-
Role of Assistive Robots in the Care of Older People: Survey Study Among Medical and Nursing Students.J Med Internet Res. 2020 Aug 12;22(8):e18003. doi: 10.2196/18003. J Med Internet Res. 2020. PMID: 32784187 Free PMC article.
-
Caregiver perspectives on a smart home-based socially assistive robot for individuals with Alzheimer's disease and related dementia.Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020 Oct;15(7):789-798. doi: 10.1080/17483107.2020.1753831. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Disabil Rehabil Assist Technol. 2020. PMID: 32299272
-
Enablers and barriers to the implementation of socially assistive humanoid robots in health and social care: a systematic review.BMJ Open. 2020 Jan 9;10(1):e033096. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-033096. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 31924639 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Towards human-centered AI and robotics to reduce hospital falls: finding opportunities to enhance patient-nurse interactions during toileting.Front Robot AI. 2024 Jan 31;11:1295679. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2024.1295679. eCollection 2024. Front Robot AI. 2024. PMID: 38357295 Free PMC article.
-
Exoskeleton technology in nursing practice: assessing effectiveness, usability, and impact on nurses' quality of work life, a narrative review.BMC Nurs. 2024 Mar 5;23(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-01821-3. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38443892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adoption of Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Robots in Long-Term Care Homes by Health Care Providers: Scoping Review.JMIR Aging. 2024 Aug 27;7:e55257. doi: 10.2196/55257. JMIR Aging. 2024. PMID: 39190455 Free PMC article.
-
The Increasing Centrality of Robotic Technology in the Context of Nursing Care: Bioethical Implications Analyzed through a Scoping Review Approach.J Healthc Eng. 2021 Aug 28;2021:1478025. doi: 10.1155/2021/1478025. eCollection 2021. J Healthc Eng. 2021. PMID: 34493953 Free PMC article.
-
Acceptance of a robotic system for nursing care: a cross-sectional survey with professional nurses, care recipients and relatives.BMC Nurs. 2024 Mar 14;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12912-024-01849-5. BMC Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38486244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertone G, Allen S, Redpath A. Ageing Europe. 2019 ed, Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union; (2019).
-
- United Nations . World Population Ageing. United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs; (2019).
-
- Kumar ES, Sachin P, Vignesh BP, Ahmed MR. Architecture for IOT based geriatric care fall detection and prevention. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (Madurai: ICICCS; ). (2017). p. 1099–104.
-
- Christoforou EG, Panayides AS, Avgousti S, Masouras P, Pattichis CS. An overview of assistive robotics and technologies for elderly care. IFMBE Proc. (2020) 76:971–6. 10.1007/978-3-030-31635-8_118 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

