Spontaneously Generated Online Patient Experience of Modafinil: A Qualitative and NLP Analysis
- PMID: 34713085
- PMCID: PMC8521895
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2021.598431
Spontaneously Generated Online Patient Experience of Modafinil: A Qualitative and NLP Analysis
Abstract
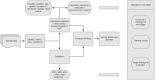
Objective: To compare the findings from a qualitative and a natural language processing (NLP) based analysis of online patient experience posts on patient experience of the effectiveness and impact of the drug Modafinil. Methods: Posts (n = 260) from 5 online social media platforms where posts were publicly available formed the dataset/corpus. Three platforms asked posters to give a numerical rating of Modafinil. Thematic analysis: data was coded and themes generated. Data were categorized into PreModafinil, Acquisition, Dosage, and PostModafinil and compared to identify each poster's own view of whether taking Modafinil was linked to an identifiable outcome. We classified this as positive, mixed, negative, or neutral and compared this with numerical ratings. NLP: Corpus text was speech tagged and keywords and key terms extracted. We identified the following entities: drug names, condition names, symptoms, actions, and side-effects. We searched for simple relationships, collocations, and co-occurrences of entities. To identify causal text, we split the corpus into PreModafinil and PostModafinil and used n-gram analysis. To evaluate sentiment, we calculated the polarity of each post between -1 (negative) and +1 (positive). NLP results were mapped to qualitative results. Results: Posters had used Modafinil for 33 different primary conditions. Eight themes were identified: the reason for taking (condition or symptom), impact of symptoms, acquisition, dosage, side effects, other interventions tried or compared to, effectiveness of Modafinil, and quality of life outcomes. Posters reported perceived effectiveness as follows: 68% positive, 12% mixed, 18% negative. Our classification was consistent with poster ratings. Of the most frequent 100 keywords/keyterms identified by term extraction 88/100 keywords and 84/100 keyterms mapped directly to the eight themes. Seven keyterms indicated negation and temporal states. Sentiment was as follows 72% positive sentiment 4% neutral 24% negative. Matching of sentiment between the qualitative and NLP methods was accurate in 64.2% of posts. If we allow for one category difference matching was accurate in 85% of posts. Conclusions: User generated patient experience is a rich resource for evaluating real world effectiveness, understanding patient perspectives, and identifying research gaps. Both methods successfully identified the entities and topics contained in the posts. In contrast to current evidence, posters with a wide range of other conditions found Modafinil effective. Perceived causality and effectiveness were identified by both methods demonstrating the potential to augment existing knowledge.
Keywords: causality; effectiveness; evidence-based medicine; natural language processing; patient experience; qualitative/NLP comparison; sentiment analysis; social media.
Copyright © 2021 Walsh, Cave and Griffiths.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Combining Topic Modeling, Sentiment Analysis, and Corpus Linguistics to Analyze Unstructured Web-Based Patient Experience Data: Case Study of Modafinil Experiences.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Dec 11;26:e54321. doi: 10.2196/54321. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39662896 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of Patient Sentiment and Emotion in Ophthalmology: Infoveillance Tutorial on Web-Based Health Forum Discussions.J Med Internet Res. 2021 May 17;23(5):e20803. doi: 10.2196/20803. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 33999001 Free PMC article.
-
Educational and Emotional Needs of Patients with Myelodysplastic Syndromes: An AI Analysis of Multi-Country Social Media.Adv Ther. 2023 Jan;40(1):159-173. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02277-0. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Adv Ther. 2023. PMID: 36136244 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of natural language processing and text mining of symptoms from electronic patient-authored text data.Int J Med Inform. 2019 May;125:37-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Int J Med Inform. 2019. PMID: 30914179 Free PMC article.
-
Natural language processing of symptoms documented in free-text narratives of electronic health records: a systematic review.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019 Apr 1;26(4):364-379. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocy173. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30726935 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of the Erectile Dysfunction Drugs Sildenafil and Tadalafil Using Patient Medication Reviews: Topic Modeling Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2022 Feb 28;10(2):e32689. doi: 10.2196/32689. JMIR Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 35225813 Free PMC article.
-
Opinion Mining of Erowid's Experience Reports on LSD and Psilocybin-Containing Mushrooms.Drug Saf. 2025 May;48(5):559-575. doi: 10.1007/s40264-025-01530-z. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 40032797
-
Combining Topic Modeling, Sentiment Analysis, and Corpus Linguistics to Analyze Unstructured Web-Based Patient Experience Data: Case Study of Modafinil Experiences.J Med Internet Res. 2024 Dec 11;26:e54321. doi: 10.2196/54321. J Med Internet Res. 2024. PMID: 39662896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dewing C, Jones T. Future of Patient Data. London: Future Agenda; (2018).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources