Targeting Oncogenic Src Homology 2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase 2 (SHP2) by Inhibiting Its Protein-Protein Interactions
- PMID: 34714648
- PMCID: PMC8591604
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.1c01371
Targeting Oncogenic Src Homology 2 Domain-Containing Phosphatase 2 (SHP2) by Inhibiting Its Protein-Protein Interactions
Abstract
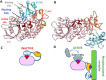
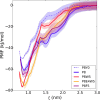
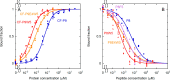
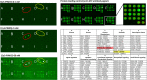
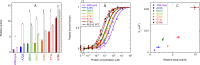
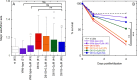
We developed a new class of inhibitors of protein-protein interactions of the SHP2 phosphatase, which is pivotal in cell signaling and represents a central target in the therapy of cancer and rare diseases. Currently available SHP2 inhibitors target the catalytic site or an allosteric pocket but lack specificity or are ineffective for disease-associated SHP2 mutants. Considering that pathogenic lesions cause signaling hyperactivation due to increased levels of SHP2 association with cognate proteins, we developed peptide-based molecules with nanomolar affinity for the N-terminal Src homology domain of SHP2, good selectivity, stability to degradation, and an affinity for pathogenic variants of SHP2 that is 2-20 times higher than for the wild-type protein. The best peptide reverted the effects of a pathogenic variant (D61G) in zebrafish embryos. Our results provide a novel route for SHP2-targeted therapies and a tool for investigating the role of protein-protein interactions in the function of SHP2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): L.S., B.B., G.B., S.M., and M.T. are the inventors of a patent application, filed by the University of Rome Tor Vergata and the Ospedale Pediatrico Bambino Gesù, regarding the molecules described in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Tartaglia M.; Martinelli S.; Cazzaniga G.; Cordeddu V.; Iavarone I.; Spinelli M.; Palmi C.; Carta C.; Pession A.; Aricò M.; Masera G.; Basso G.; Sorcini M.; Gelb B.; Biondi A. Genetic evidence for lineage-related and differentiation stage-related contribution of somatic PTPN11 mutations to leukemogenesis in childhood acute leukemia. Blood 2004, 104, 307–313. 10.1182/blood-2003-11-3876. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen Y. N.; LaMarche M. J.; Chan H. M.; Fekkes P.; Garcia-Fortanet J.; Acker M. G.; Antonakos B.; Chen C. H.; Chen Z.; Cooke V. G.; Dobson J. R.; Deng Z.; Fei F.; Firestone B.; Fodor M.; Fridrich C.; Gao H.; Grunenfelder D.; Hao H. X.; Jacob J.; Ho S.; Hsiao K.; Kang Z. B.; Karki R.; Kato M.; Larrow J.; La Bonte L. R.; Lenoir F.; Liu G.; Liu S.; Majumdar D.; Meyer M. J.; Palermo M.; Perez L.; Pu M.; Price E.; Quinn C.; Shakya S.; Shultz M. D.; Slisz J.; Venkatesan K.; Wang P.; Warmuth M.; Williams S.; Yang G.; Yuan J.; Zhang J. H.; Zhu P.; Ramsey T.; Keen N. J.; Sellers W. R.; Stams T.; Fortin P. D. Allosteric inhibition of SHP2 phosphatase inhibits cancers driven by receptor tyrosine kinases. Nature 2016, 535, 148–152. 10.1038/nature18621. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

