A critical review of bile acids and their receptors in hepatic encephalopathy
- PMID: 34715070
- PMCID: PMC9798441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ab.2021.114436
A critical review of bile acids and their receptors in hepatic encephalopathy
Abstract
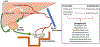
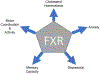
Hepatic encephalopathy describes an array of neurological complications that arise due to liver insufficiency. The pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy shares a longstanding association with hyperammonemia and inflammation, and recently, aberrant bile acid signaling has been implicated in the development of key features of hepatic encephalopathy. These key features include neuronal dysfunction, neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier permeability. This review summarizes the findings of recent studies demonstrating a role for bile acids in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy via one of three main bile acid receptors and speculates on the possible downstream consequences of aberrant bile acid signaling.
Keywords: Cholesterol homeostasis; FXR; Neuroinflammation; Neurosteroids; S1P2R; TGR5.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have none to declare.
Figures
References
-
- American Association for the Study of Liver D, European Association for the Study of the L. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 practice guideline by the European Association for the Study of the Liver and the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. J Hepatol 2014;61:642–59. - PubMed
-
- Romero-Gomez M, Montagnese S, Jalan R. Hepatic encephalopathy in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis and acute-on-chronic liver failure. J Hepatol 2015;62:437–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

