Immunoprofiling of early, untreated rheumatoid arthritis using mass cytometry reveals an activated basophil subset inversely linked to ACPA status
- PMID: 34715910
- PMCID: PMC8555233
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-021-02630-8
Immunoprofiling of early, untreated rheumatoid arthritis using mass cytometry reveals an activated basophil subset inversely linked to ACPA status
Abstract
Background: Autoantibody production is a hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA) are highly disease-specific, and their presence is associated with more severe disease and poor prognosis compared to ACPA-negative patients. However, the immune cell composition associated with antibody-positive/negative disease is incompletely defined. Mass cytometry (MC) is a high-dimensional technique offering new possibilities in the determination of the immune cell composition in rheumatic diseases. Here, we set up a broad phenotyping panel to study the immune cell profile of early untreated RA to investigate if specific immune cell subsets are associated with ACPA+ versus ACPA- RA.
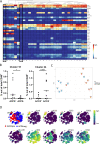
Methods: Freshly obtained PBMCs of early, untreated RA patients (8 ACPA+ and 7 ACPA-) were analysed using a 36-marker MC panel, including markers related to various immune lineages. Data were processed using Cytosplore for dimensional reduction (HSNE) and clustering. Groups were compared using Cytofast. A second validation cohort of cryopreserved PBMCs obtained from early RA patients (27 ACPA+ and 20 ACPA-) was used to confirm MC data by flow cytometry (FC). FC data were processed and analysed using both an unsupervised analysis pipeline and through manual gating.
Results: MC indicated no differences when comparing major immune lineages (i.e. monocytes, T and B cells), but highlighted two innate subsets: CD62L+ basophils (p = 0.33) and a subset of CD16- NK cells (p = 0.063). Although the NK cell subset did not replicate by FC, FC replication confirmed the difference in CD62L+ basophil frequency when comparing ACPA+ to ACPA- patients (mean 0.32% vs. 0.13%; p = 0.01).
Conclusions: Although no differences in major lineages were found between early ACPA+ and ACPA- RA, this study identified the reduced presence of activated basophils in ACPA-negative disease as compared to ACPA-positive disease and thereby provides the first evidence for a connection between activated basophils and ACPA status.
Keywords: Basophils; CD62L; Immune-profiling; Mass cytometry; Rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
HK has performed this work as part of her PhD studies and is currently an employee of Fluidigm. GB is currently an employee of VisuaLyte.
Figures


References
-
- Fonseka CY, et al. Mixed-effects association of single cells identifies an expanded effector CD4+ T cell subset in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018;10. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30333237/. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Matthijssen XME, Niemantsverdriet E, Huizinga TWJ, van der Helm-van Mil AHM. Enhanced treatment strategies and distinct disease outcomes among autoantibody-positive and -negative rheumatoid arthritis patients over 25 years: a longitudinal cohort study in the Netherlands. PLoS Med. 2020;17:e1003296. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003296. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

