Dysregulation of RNA interference components in COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 34715923
- PMCID: PMC8554738
- DOI: 10.1186/s13104-021-05816-0
Dysregulation of RNA interference components in COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Objective: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is the novel coronavirus causing severe respiratory illness (COVID-19). This virus was initially identified in Wuhan city, a populated area of the Hubei province in China, and still remains one of the major global health challenges. RNA interference (RNAi) is a mechanism of post-transcriptional gene silencing that plays a crucial role in innate viral defense mechanisms by inhibiting the virus replication as well as expression of various viral proteins. Dicer, Drosha, Ago2, and DGCR8 are essential components of the RNAi system, which is supposed to be dysregulated in COVID-19 patients. This study aimed to assess the expression level of the mentioned mRNAs in COVID-19patients compared to healthy individuals.
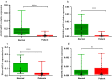
Results: Our findings demonstrated that the expression of Dicer, Drosha, and Ago2 was statistically altered in COVID-19 patients compared to healthy subjects. Ultimately, the RNA interference mechanism as a crucial antiviral defense system was suggested to be dysregulated in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: Ago2; DGCR8; Dicer; Drosha; RNA interference; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kumar S, Nyodu R, Maurya VK, Saxena SK. Morphology, genome organization, replication, and pathogenesis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Springer; 2020. pp. 23–31.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

