Anti-GD2 IgA kills tumors by neutrophils without antibody-associated pain in the preclinical treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma
- PMID: 34716207
- PMCID: PMC8559241
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003163
Anti-GD2 IgA kills tumors by neutrophils without antibody-associated pain in the preclinical treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma
Abstract
Background: The addition of monoclonal antibody therapy against GD2 to the treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma led to improved responses in patients. Nevertheless, administration of GD2 antibodies against neuroblastoma is associated with therapy-limiting neuropathic pain. This severe pain is evoked at least partially through complement activation on GD2-expressing sensory neurons.
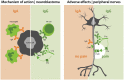
Methods: To reduce pain while maintaining antitumor activity, we have reformatted the approved GD2 antibody ch14.18 into the IgA1 isotype. This novel reformatted IgA is unable to activate the complement system but efficiently activates leukocytes through the FcαRI (CD89).
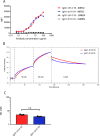
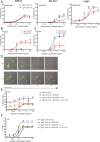
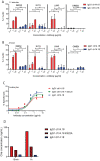
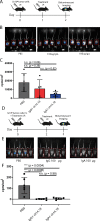
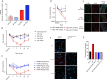
Results: IgA GD2 did not activate the complement system in vitro nor induced pain in mice. Importantly, neutrophil-mediated killing of neuroblastoma cells is enhanced with IgA in comparison to IgG, resulting in efficient tumoricidal capacity of the antibody in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusions: Our results indicate that employing IgA GD2 as a novel isotype has two major benefits: it halts antibody-induced excruciating pain and improves neutrophil-mediated lysis of neuroblastoma. Thus, we postulate that patients with high-risk neuroblastoma would strongly benefit from IgA GD2 therapy.
Keywords: immunotherapy; neuroblastoma; pain; pediatrics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JL is co-founder of TigaTx and ME is employed by TigaTx.
Figures
References
-
- Gilman AL, Ozkaynak MF, Matthay KK, et al. . Phase I study of ch14.18 with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and interleukin-2 in children with neuroblastoma after autologous bone marrow transplantation or stem-cell rescue: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol 2009;27:85–91. 10.1200/JCO.2006.10.3564 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
