The role of PI3'-lipid signalling in melanoma initiation, progression and maintenance
- PMID: 34717019
- PMCID: PMC8724390
- DOI: 10.1111/exd.14489
The role of PI3'-lipid signalling in melanoma initiation, progression and maintenance
Abstract
Phosphatidylinositol-3'-kinases (PI3Ks) are a family of lipid kinases that phosphorylate the 3' hydroxyl (OH) of the inositol ring of phosphatidylinositides (PI). Through their downstream effectors, PI3K generated lipids (PI3K-lipids hereafter) such as PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(3,4)P2 regulate myriad biochemical and biological processes in both normal and cancer cells including responses to growth hormones and cytokines; the cell division cycle; cell death; cellular growth; angiogenesis; membrane dynamics; and autophagy and many aspects of cellular metabolism. Engagement of receptor tyrosine kinase by their cognate ligands leads to activation of members of the Class I family of PI3'-kinases (PI3Kα, β, δ & γ) leading to accumulation of PI3K-lipids. Importantly, PI3K-lipid accumulation is antagonized by the hydrolytic action of a number of PI3K-lipid phosphatases, most notably the melanoma suppressor PTEN (lipid phosphatase and tensin homologue). Downstream of PI3K-lipid production, the protein kinases AKT1-3 are believed to be key effectors of PI3'-kinase signalling in cells. Indeed, in preclinical models, activation of the PI3K→AKT signalling axis cooperates with alterations such as expression of the BRAFV600E oncoprotein kinase to promote melanoma progression and metastasis. In this review, we describe the different classes of PI3K-lipid effectors, and how they may promote melanomagenesis, influence the tumour microenvironment, melanoma maintenance and progression to metastatic disease. We also provide an update on both FDA-approved or experimental inhibitors of the PI3K→AKT pathway that are currently being evaluated for the treatment of melanoma either in preclinical models or in clinical trials.
Keywords: biomarkers; cancer; melanogenesis; melanoma.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTERESTS
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
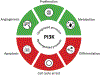

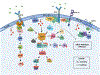
References
-
- Whitman M, Kaplan DR, Schaffhausen B, Cantley L, Roberts TM. Association of phosphatidylinositol kinase activity with polyoma middle-T competent for transformation. Nature. 1985;315(6016):239–242. - PubMed
-
- Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC. The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(8):606–619. - PubMed
-
- Vivanco I, Sawyers CL. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2(7):489–501. - PubMed
-
- Katso R, Okkenhaug K, Ahmadi K, White S, Timms J, Waterfield MD. Cellular function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases: implications for development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2001;17:615–675. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

