The negative impact of T cell-mediated rejection on renal allograft survival in the modern era
- PMID: 34717048
- PMCID: PMC9299170
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16883
The negative impact of T cell-mediated rejection on renal allograft survival in the modern era
Abstract
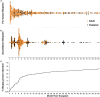
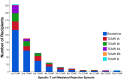
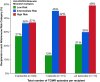
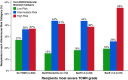
The prevalence and long-term impact of T cell-mediated rejection (TCMR) is poorly defined in the modern era of tacrolimus/mycophenolate-based maintenance therapy. This observational study evaluated 775 kidney transplant recipients with serial histology and correlated TCMR events with the risk of graft loss. After a ~30% incidence of a first Banff Borderline or greater TCMR detected on for-cause (17%) or surveillance (13%) biopsies, persistent (37.4%) or subsequent (26.3%) TCMR occurred in 64% of recipients on follow-up biopsies. Alloimmune risk categories based on the HLA-DR/DQ single molecule eplet molecular mismatch correlated with the number of TCMR events (p = .002) and Banff TCMR grade (p = .007). Both a first and second TCMR event correlated with death-censored and all-cause graft loss when adjusted for baseline covariates and other significant time-dependent covariates such as DGF and ABMR. Therefore, a substantial portion of kidney transplant recipients, especially those with intermediate and high HLA-DR/DQ molecular mismatch scores, remain under-immunosuppressed, which in turn identifies the need for novel agents that can more effectively prevent or treat TCMR.
Keywords: T cell-mediated rejection; antibody-mediated rejection; clinical research/practice; graft survival; histocompatibility; immunosuppression/immune modulation; kidney transplantation; patient survival.
© 2021 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures


Comment in
-
Revisiting acute T cell-mediated rejection in kidney allografts.Am J Transplant. 2022 Mar;22(3):681-682. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16923. Epub 2021 Dec 18. Am J Transplant. 2022. PMID: 34897977 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nankivell BJ, Borrows RJ, Fung CL‐S, O’Connell PJ, Allen RDM, Chapman JR. Natural history, risk factors, and impact of subclinical rejection in kidney transplantation. Transplant J. 2004;78(2):242‐249. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000128167.60172.cc - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

