Influence of Disease Activity and Body Composition Parameters on Cross-Sectional Area of the Median Nerve in Acromegalic Patients
- PMID: 34717059
- PMCID: PMC8815471
- DOI: 10.33549/physiolres.934681
Influence of Disease Activity and Body Composition Parameters on Cross-Sectional Area of the Median Nerve in Acromegalic Patients
Abstract
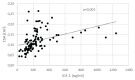
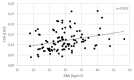
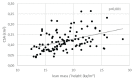
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is neuropathy that occurs due to compression of the median nerve in the carpal tunnel. Acromegaly is one of the important causes of CTS. The aim of this study was to examine median nerve with ultrasound in acromegalic patients and to assess the relationship with activity, duration of disease and body composition parameters. We prospectively examined the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the median nerve with high-resolution ultrasound in 107 acromegalic patients (70 females and 37 males) and 107 healthy controls (70 females and 37 males) matched for age, gender, and BMI. Body composition parameters were assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA). The Student t-tests and Pearson correlation were used for data analysis. The cross sectional area of the median nerve was increased in acromegalic patients compared to controls (11.9 ± 4.8 mm2 vs. 7.7 ± 2.4 mm2, P < 0.001). Positive correlation was found between IGF-1 levels and CSA in the acromegalic group (R = 0.400, P < 0.001). Relationship between CSA and duration of acromegaly was not confirmed. In acromegalic patients, BMI correlated with the CSA (R = 0.294, P = 0.002). There was no significant difference in BMI, fat mass between the acromegalic and control group, but lean mass was higher in acromegalic patients compared with controls (54.8 ± 13.3 vs. 51 ± 11.6, P = 0.047). Lean mass and LMI (total body lean mass/height) positively correlated with CSA in acromegalic patients (R = 0.340, P < 0.001; R = 0.424, P < 0.001). No correlation was observed between fat mass and CSA of median nerve in all groups. We confirmed the enlargement of the median nerve in acromegalic patients. This enlargement is proportional to the degree of IGF-1 levels and is not dependent on the duration of the disease. The enlargement of the median nerve in acromegalic patients also depends on lean body mass and is not dependent on fat body mass.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in Cross-Sectional Area of the Median Nerve and Body Composition Parameters after Treatment of Acromegaly: 1 year Follow-Up.Int J Endocrinol. 2022 Oct 13;2022:8766046. doi: 10.1155/2022/8766046. eCollection 2022. Int J Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36277124 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound measurement of median and ulnar nerve cross-sectional area in acromegaly.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008 Mar;93(3):905-9. doi: 10.1210/jc.2007-1719. Epub 2007 Dec 11. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008. PMID: 18073306
-
Ultrasound of peripheral nerves in acromegaly: changes at 1-year follow-up.Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009 Aug;71(2):220-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03468.x. Epub 2008 Nov 3. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009. PMID: 19178522
-
Diagnostic potential of ultrasound in carpal tunnel syndrome with different etiologies: correlation of sonographic median nerve measures with electrodiagnostic severity.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019 Dec 29;20(1):634. doi: 10.1186/s12891-019-3010-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019. PMID: 31884951 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic utility of ultrasonography versus nerve conduction studies in mild carpal tunnel syndrome.Arthritis Rheum. 2008 Mar 15;59(3):357-66. doi: 10.1002/art.23317. Arthritis Rheum. 2008. PMID: 18311762 Review.
Cited by
-
Changes in Cross-Sectional Area of the Median Nerve and Body Composition Parameters after Treatment of Acromegaly: 1 year Follow-Up.Int J Endocrinol. 2022 Oct 13;2022:8766046. doi: 10.1155/2022/8766046. eCollection 2022. Int J Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 36277124 Free PMC article.
-
Filling the gap between the heart and the body in acromegaly: a case-control study.Endocrine. 2023 Feb;79(2):365-375. doi: 10.1007/s12020-022-03232-3. Epub 2022 Oct 30. Endocrine. 2023. PMID: 36309947 Free PMC article.
-
Age, body composition parameters and glycaemic control contribute to trabecular bone score deterioration in acromegaly more than disease activity.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 21;14:1197725. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1197725. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37670889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BRUMBACK RA, BARR CE. Myopathy in acromegaly. A case study. Pathol Res Pract. 1983;177:41–46. - PubMed
-
- DALILI AR, MARDANI KM, ALIZADEH A, HATAMIAN HR, HOSEININEJAD N, PEYRAZM H. Comparison between sonography and electrodiagnostic testing in the diagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Anesthesiol Pain. 2011;2:43–51.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
