Combined cART including Tenofovir Disoproxil, Emtricitabine, and Dolutegravir has potent therapeutic effects in HIV-1 infected humanized mice
- PMID: 34717655
- PMCID: PMC8557591
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-021-03120-w
Combined cART including Tenofovir Disoproxil, Emtricitabine, and Dolutegravir has potent therapeutic effects in HIV-1 infected humanized mice
Abstract
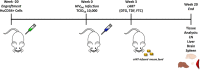
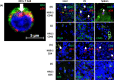
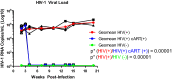
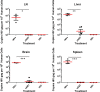
HIV-1 reservoirs persist in the presence of combined antiretroviral therapy (cART). However, cART has transformed HIV-1 infection into a chronic disease marked by control of HIV-1 viral load and mortality reduction. Major challenges remain, including viral resistance upon termination of cART and persistence and identification of tissue distribution of HIV-1 reservoirs. Thus, appropriate animal models that best mimic HIV-1 pathogenesis are important, and the current study complements our previously published validation of the CD34+ hematopoietic humanized mouse model for this purpose. Here we analyze viral suppression using the recently developed combination of antiretrovirals that include Tenofovir Disoproxil (TDF), Emtricitabine (FTC), and Dolutegravir (DTG), a choice based on recent clinical outcomes showing its improved antiretroviral potency, CD4+ T cell preservation, tolerability, and prevention of viral drug resistance compared to that of previous regimens. We used quantitative Airyscan-based super resolution confocal microscopy of selected mouse tissues. Our data allowed us to identify specific solid tissue reservoirs of human T cells expressing the HIV-1 core protein p24. In particular, lymph node, brain, spleen, and liver were visualized as reservoirs for residual infected cells. Marked reduction of viral replication was evident. Considering that detection and visualization of cryptic sites of HIV-1 infection in tissues are clearly crucial steps towards HIV-1 eradication, appropriate animal models with pseudo-human immune systems are needed. In fact, current studies with humans and non-human primates have limited sample availability at multiple stages of infection and cannot easily analyze the effects of differently administered combined antiretroviral treatments on multiple tissues. That is easier to manage when working with humanized mouse models, although we realize the limitations due to low human cell recovery and thus the number of cells available for thorough and comprehensive analyses. Nonetheless, our data further confirm that the CD34+ humanized mouse model is a potentially useful pre-clinical model to study and improve current anti-HIV-1 therapies.
Keywords: Antiretroviral therapies; HIV/AIDS pathogenesis; Hu-mouse models.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dolutegravir + Lamivudine vs. Dolutegravir + Tenofovir Disoproxil Fumarate/Emtricitabine: Very-Low-Level HIV-1 Replication through 144 Weeks in the GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2 Studies.Viruses. 2024 Mar 6;16(3):405. doi: 10.3390/v16030405. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543770 Free PMC article.
-
Dolutegravir with emtricitabine and tenofovir alafenamide or tenofovir disoproxil fumarate versus efavirenz, emtricitabine, and tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for initial treatment of HIV-1 infection (ADVANCE): week 96 results from a randomised, phase 3, non-inferiority trial.Lancet HIV. 2020 Oct;7(10):e666-e676. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30241-1. Lancet HIV. 2020. PMID: 33010240 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of switching to dolutegravir plus emtricitabine/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF) or elvitegravir/cobicistat/emtricitabine/TDF in virologically suppressed HIV-infected patients in clinical practice: results from a multicentre, observational study.HIV Med. 2019 Feb;20(2):164-168. doi: 10.1111/hiv.12688. Epub 2018 Nov 20. HIV Med. 2019. PMID: 30457197
-
Abacavir/dolutegravir/lamivudine single-tablet regimen: a review of its use in HIV-1 infection.Drugs. 2015 Apr;75(5):503-14. doi: 10.1007/s40265-015-0361-6. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25698454 Review.
-
Increased viral load in a hospitalized patient on treatment with crushed bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide: A case report and review of the literature.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022 Aug 5;79(16):1330-1336. doi: 10.1093/ajhp/zxac120. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2022. PMID: 35511892 Review.
Cited by
-
The Humanized Mouse Model: What Added Value Does It Offer for HIV Research?Pathogens. 2023 Apr 17;12(4):608. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12040608. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37111494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Host microRNAomics in HIV Infections: Therapeutic Potentials and Limitations.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8809. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168809. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201495 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cannabis Use in HIV: Impact on Inflammation, Immunity and the Microbiome.Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025 Feb 22;22(1):19. doi: 10.1007/s11904-025-00729-0. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2025. PMID: 39984806 Review.
-
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling Studies of New 8-methyl-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carbohydrazides as Potential Anti-HIV Agents.Iran J Pharm Res. 2022 May 17;21(1):e123962. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-123962. eCollection 2022 Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 36060911 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

