Risk factors for secondary fractures to percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review
- PMID: 34717682
- PMCID: PMC8556988
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-021-02722-w
Risk factors for secondary fractures to percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a systematic review
Abstract
Background: Osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture (OVCF) is one of the most common fragile fractures, and percutaneous vertebroplasty provides considerable long-term benefits. At the same time, there are many reports of postoperative complications, among which fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty is one of the complications after vertebroplasty (PVP). Although there are many reports on the risk factors of secondary fracture after PVP at home and abroad, there is no systematic analysis on the related factors of secondary fracture after PVP.
Methods: The databases, such as CNKI, Wan Fang Database and PubMed, were searched for documents on secondary fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty published at home and abroad from January 2011 to March 2021. After strictly evaluating the quality of the included studies and extracting data, a meta-analysis was conducted by using Revman 5.3 software.
Results: A total of 9 articles were included, involving a total of 1882 patients, 340 of them diagnosed as secondary fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty.
Conclusion: The additional history of fracture, age, bone mineral density (BMD), bone cement leakage, intravertebral fracture clefts and Cobb Angle might be risk factors related to secondary fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. The height of vertebral anterior and body mass index (BMI) were not correlated.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Percutaneous vertebroplasty; Risk factor; Vertebral compression fractures (VCFs).
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



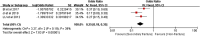
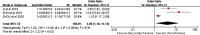
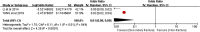

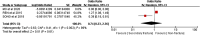

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

