Lower Serologic Response to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Treated With Anti-TNFα
- PMID: 34717923
- PMCID: PMC8552587
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.029
Lower Serologic Response to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Treated With Anti-TNFα
Abstract
Background & aim: Patients with inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), specifically those treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α biologics, are at high risk for vaccine-preventable infections. Their ability to mount adequate vaccine responses is unclear. The aim of the study was to assess serologic responses to messenger RNA-Coronavirus Disease 2019 vaccine, and safety profile, in patients with IBD stratified according to therapy, compared with healthy controls (HCs).
Methods: Prospective, controlled, multicenter Israeli study. Subjects enrolled received 2 BNT162b2 (Pfizer/BioNTech) doses. Anti-spike antibody levels and functional activity, anti-TNFα levels and adverse events (AEs) were detected longitudinally.
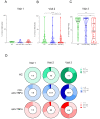
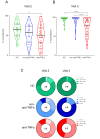
Results: Overall, 258 subjects: 185 IBD (67 treated with anti-TNFα, 118 non-anti-TNFα), and 73 HCs. After the first vaccine dose, all HCs were seropositive, whereas ∼7% of patients with IBD, regardless of treatment, remained seronegative. After the second dose, all subjects were seropositive, however anti-spike levels were significantly lower in anti-TNFα treated compared with non-anti-TNFα treated patients, and HCs (both P < .001). Neutralizing and inhibitory functions were both lower in anti-TNFα treated compared with non-anti-TNFα treated patients, and HCs (P < .03; P < .0001, respectively). Anti-TNFα drug levels and vaccine responses did not affect anti-spike levels. Infection rate (∼2%) and AEs were comparable in all groups. IBD activity was unaffected by BNT162b2.
Conclusions: In this prospective study in patients with IBD stratified according to treatment, all patients mounted serologic response to 2 doses of BNT162b2; however, its magnitude was significantly lower in patients treated with anti-TNFα, regardless of administration timing and drug levels. Vaccine was safe. As vaccine serologic response longevity in this group may be limited, vaccine booster dose should be considered.
Keywords: COVID-19; Serologic Response; Vaccine; mRNA-BNT162b2.
Copyright © 2022 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Laboratory testing for 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in suspected human cases. Interim Guidance. World Health Organization; 2020.
-
- Rahier J.F., Magro F., Abreu C., et al. Second European evidence-based consensus on the prevention, diagnosis and management of opportunistic infections in inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2014;8:443–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

