Preclinical characterization of bemarituzumab, an anti-FGFR2b antibody for the treatment of cancer
- PMID: 34719330
- PMCID: PMC8565817
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2021.1981202
Preclinical characterization of bemarituzumab, an anti-FGFR2b antibody for the treatment of cancer
Abstract
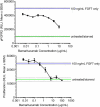
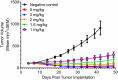
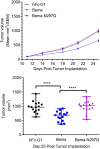
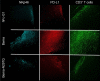
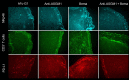
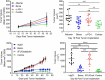
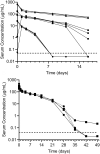
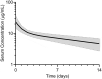
Bemarituzumab (FPA144) is a first-in-class, humanized, afucosylated immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) directed against fibroblast growth factor receptor 2b (FGFR2b) with two mechanisms of action against FGFR2b-overexpressing tumors: inhibition of FGFR2b signaling and enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Bemarituzumab is being developed as a cancer therapeutic, and we summarize here the key nonclinical data that supported moving it into clinical trials. Bemarituzumab displayed sub-nanomolar cross-species affinity for FGFR2b receptors, with >20-fold enhanced binding affinity to human Fc gamma receptor IIIa compared with the fucosylated version. In vitro, bemarituzumab induced potent ADCC against FGFR2b-expressing tumor cells, and inhibited FGFR2 phosphorylation and proliferation of SNU-16 gastric cancer cells in a concentration-dependent manner. In vivo, bemarituzumab inhibited tumor growth through inhibition of the FGFR2b pathway and/or ADCC in mouse models. Bemarituzumab demonstrated enhanced anti-tumor activity in combination with chemotherapy, and due to bemarituzumab-induced natural killer cell-dependent increase in programmed death-ligand 1, also resulted in enhanced anti-tumor activity when combined with an anti-programmed death-1 antibody. Repeat-dose toxicity studies established the highest non-severely-toxic dose at 1 and 100 mg/kg in rats and cynomolgus monkeys, respectively. In pharmacokinetic (PK) studies, bemarituzumab exposure increase was greater than dose-proportional, with the linear clearance in the expected dose range for a mAb. The PK data in cynomolgus monkeys were used to project bemarituzumab linear PK in humans, which were consistent with the observed human Phase 1 data. These key nonclinical studies facilitated the successful advancement of bemarituzumab into the clinic.
Keywords: Bemarituzumab; afucosylated antibody; antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytoxicity; phosphorylation in vitro; anti-FGFR2b antibody; anti-tumor efficacy; cell proliferation in vitro; fibroblast growth factor receptor; pharmacokinetics; toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
This research was sponsored by FivePrime. All authors other than Rong Deng were employees of FivePrime and had a business and/or financial interest in the company. Rong Deng declare no potential conflicts of interest. Medical writing services were funded by FivePrime. Five Prime was acquired by Amgen Inc. on April 16th, 2021.
Figures


References
-
- Hattori Y, Odagiri H, Nakatani H, Miyagawa K, Naito K, Sakamoto H, Katoh O, Yoshida T, Sugimura T, Terada M. K-sam, an amplified gene in stomach cancer, is a member of the heparin-binding growth factor receptor genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1990;87(15):5983–87. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.15.5983. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
