Upregulation of lncRNA NONRATG019935.2 suppresses the p53-mediated apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in septic acute kidney injury
- PMID: 34719669
- PMCID: PMC8558325
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-03953-9
Upregulation of lncRNA NONRATG019935.2 suppresses the p53-mediated apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells in septic acute kidney injury
Abstract
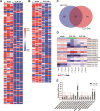
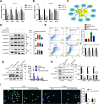
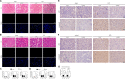
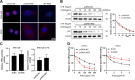
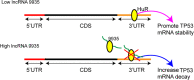
Although increasing evidence has confirmed that the apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells (RTECs) is a crucial contributor to the onset and development of septic acute kidney injury (AKI), the pathological mechanism by which RTEC apoptosis is upregulated during septic AKI is not entirely clear. In this study, a rat model of septic AKI was induced by a cecal ligation puncture procedure or lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection. Four differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs (DE-Lncs) in the rat model of septic AKI were determined using RNA-sequencing and verified by qRT-PCR. Among the four DE-Lncs, the expression level of lncRNA NONRATG019935.2 (9935) exhibited the most significant reduction in both septic AKI rats and LPS-treated NRK-52E cells (a rat RTEC line). The overexpression of 9935 suppressed cell apoptosis and p53 protein level in LPS-treated NRK-52E cells, and retarded septic AKI development in the rat model of septic AKI. Mechanistically, 9935 decreased the human antigen R (HuR)-mediated Tp53 mRNA stability by limiting the combination of HuR and the 3'UTR region of Tp53 mRNA in RTECs. The overexpression of HuR abrogated the inhibitory effect of pcDNA-9935 on the LPS-induced apoptosis of NRK-52E and rat primary RTECs. In conclusion, 9935 exerts its role in septic AKI by suppressing the p53-mediated apoptosis of RTECs, and this essential role of 9935 relies on its destructive effect on HuR-mediated Tp53 mRNA stability.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Usp9x contributes to the development of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting inflammation and apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via activation of the TLR4/nf-κb pathway.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2361089. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2361089. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38874156 Free PMC article.
-
Long Non-Coding RNA RMRP Contributes to Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.Yonsei Med J. 2021 Mar;62(3):262-273. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2021.62.3.262. Yonsei Med J. 2021. PMID: 33635017 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog-induced putative kinase 1-Parkin-mediated mitophagy in septic acute kidney injury.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Oct 5;132(19):2340-2347. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000448. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 31567378 Free PMC article.
-
EP300-mediated H3 acetylation elevates MTHFD2 expression to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-induced tubular epithelial cells.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2369342. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2369342. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 39230047 Free PMC article.
-
Acute kidney injury: a paradigm for miRNA regulation of the cell cycle.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Aug;42(4):1219-23. doi: 10.1042/BST20140093. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25110028 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA ENSMUST00000171502 Induced by HIF-1α Ameliorates Ischemic Acute Kidney Injury via Targeting the miR-130b-3p/Mybl-1 Axis.Cells. 2022 Nov 23;11(23):3747. doi: 10.3390/cells11233747. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497007 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of non-coding RNAs in acute kidney injury: a focus on natural medicine treatment.Front Mol Biosci. 2025 Aug 7;12:1648526. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2025.1648526. eCollection 2025. Front Mol Biosci. 2025. PMID: 40852498 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Usp9x contributes to the development of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting inflammation and apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells via activation of the TLR4/nf-κb pathway.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(2):2361089. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2361089. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38874156 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 exaggerates multiple organ injury, inflammation, and immune cell imbalance by activating the NF-κB pathway in sepsis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 7;14:1117285. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1117285. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36960276 Free PMC article.
-
An Update of Long-Noncoding RNAs in Acute Kidney Injury.Front Physiol. 2022 Mar 8;13:849403. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.849403. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35350698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

