Fitbeat: COVID-19 estimation based on wristband heart rate using a contrastive convolutional auto-encoder
- PMID: 34720200
- PMCID: PMC8547790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2021.108403
Fitbeat: COVID-19 estimation based on wristband heart rate using a contrastive convolutional auto-encoder
Abstract
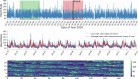
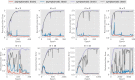
This study proposes a contrastive convolutional auto-encoder (contrastive CAE), a combined architecture of an auto-encoder and contrastive loss, to identify individuals with suspected COVID-19 infection using heart-rate data from participants with multiple sclerosis (MS) in the ongoing RADAR-CNS mHealth research project. Heart-rate data was remotely collected using a Fitbit wristband. COVID-19 infection was either confirmed through a positive swab test, or inferred through a self-reported set of recognised symptoms of the virus. The contrastive CAE outperforms a conventional convolutional neural network (CNN), a long short-term memory (LSTM) model, and a convolutional auto-encoder without contrastive loss (CAE). On a test set of 19 participants with MS with reported symptoms of COVID-19, each one paired with a participant with MS with no COVID-19 symptoms, the contrastive CAE achieves an unweighted average recall of , a sensitivity of and a specificity of , an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) of 0.944, indicating a maximum successful detection of symptoms in the given heart rate measurement period, whilst at the same time keeping a low false alarm rate.
Keywords: Anomaly detection; COVID-19; Contrastive learning; Convolutional auto-encoder; Respiratory tract infection.
© 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Ranjan Y., Rashid Z., Stewart C., Conde P., Begale M., Verbeeck D., Boettcher S., Hyve T., Dobson R., Folarin A., Consortium T.R.-C. RADAR-base: open source mobile health platform for collecting, monitoring, and analyzing data using sensors, wearables, and mobile devices. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019;7(8):13pages. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohammadi M., Al-Fuqaha A., Sorour S., Guizani M. Deep Learning for IoT big data and streaming analytics: a survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2018;20(4):2923–2960.
-
- Quer G., Radin J., Gadaleta M., Baca-Motes K., Ariniello L., Ramos E., Kheterpal V., Topol E., Steinhubl S. Wearable sensor data and self-reported symptoms for COVID-19 detection. Nat. Med. 2020;2:1–5. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
