Comparison of the Characteristics of Cytokine Storm and Immune Response Induced by SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 Infections
- PMID: 34720596
- PMCID: PMC8550203
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S329697
Comparison of the Characteristics of Cytokine Storm and Immune Response Induced by SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 Infections
Abstract
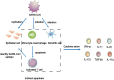
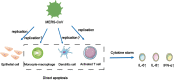
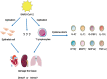
Cytokine storm (CS) is a significant cause of death in patients with severe coronavirus pneumonia. Excessive immune-inflammatory reaction, many inflammatory cell infiltration, and extreme increase of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines lead to acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). This review compares the characters of cytokine storms and immune responses caused by three highly pathogenic and infectious coronaviruses (HCoVs), including severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Middle East respiratory syndrome-coronavirus (MERS-CoV), and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), and analyzes the possible mechanisms to guide clinical treatment in the future.
Keywords: coronavirus pneumonia; cytokine storm; cytokines; immune evasion; interferon.
© 2021 Liu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

