Inhibition of Rho Kinase by Fasudil Ameliorates Cognition Impairment in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites
- PMID: 34721000
- PMCID: PMC8551711
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.755164
Inhibition of Rho Kinase by Fasudil Ameliorates Cognition Impairment in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice via Modulation of Gut Microbiota and Metabolites
Abstract
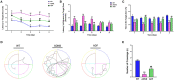
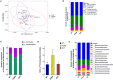
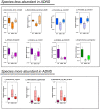
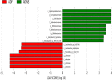
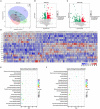
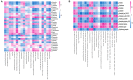
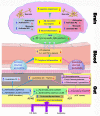
Background: Fasudil, a Rho kinase inhibitor, exerts therapeutic effects in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a chronic neurodegenerative disease with progressive loss of memory. However, the mechanisms remain unclear. In addition, the gut microbiota and its metabolites have been implicated in AD. Methods: We examined the effect of fasudil on learning and memory using the Morris water-maze (MWM) test in APPswe/PSEN1dE9 transgenic (APP/PS1) mice (8 months old) treated (i.p.) with fasudil (25 mg/kg/day; ADF) or saline (ADNS) and in age- and gender-matched wild-type (WT) mice. Fecal metagenomics and metabolites were performed to identify novel biomarkers of AD and elucidate the mechanisms of fasudil induced beneficial effects in AD mice. Results: The MWM test showed significant improvement of spatial memory in APP/PS1 mice treated with fasudil as compared to ADNS. The metagenomic analysis revealed the abundance of the dominant phyla in all the three groups, including Bacteroidetes (23.7-44%) and Firmicutes (6.4-26.6%), and the increased relative abundance ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes in ADNS (59.1%) compared to WT (31.7%). In contrast, the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio was decreased to the WT level in ADF (32.8%). Lefse analysis of metagenomics identified s_Prevotella_sp_CAG873 as an ADF potential biomarker, while s_Helicobacter_typhlonius and s_Helicobacter_sp_MIT_03-1616 as ADNS potential biomarkers. Metabolite analysis revealed the increment of various metabolites, including glutamate, hypoxanthine, thymine, hexanoyl-CoA, and leukotriene, which were relative to ADNS or ADF microbiota potential biomarkers and mainly involved in the metabolism of nucleotide, lipids and sugars, and the inflammatory pathway. Conclusions: Memory deficit in APP/PS1 mice was correlated with the gut microbiome and metabolite status. Fasudil reversed the abnormal gut microbiota and subsequently regulated the related metabolisms to normal in the AD mice. It is believed that fasudil can be a novel strategy for the treatment of AD via remodeling of the gut microbiota and metabolites. The novel results also provide valuable references for the use of gut microbiota and metabolites as diagnostic biomarkers and/or therapeutic targets in clinical studies of AD.
Keywords: APP/PS1 double transgenic AD mouse; Alzheimer's disease; Morris water maze; cognition; gut microbiota; metabolite; metagenomics.
Copyright © 2021 Yan, Gao, Fang, Zhang, Kumar, Yan, Song, Li, Zhang, Sun, Wang, Zhao, Skaggs, Zhang and Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exosomal MicroRNAs modulate the cognitive function in fasudil treated APPswe/PSEN1dE9 transgenic (APP/PS1) mice model of Alzheimer's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Oct;39(7):1335-1351. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01395-8. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39088109 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of fasudil treatment in the APPswe/PSEN1dE9 transgenic (APP/PS1) mice model of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 22;12(1):6625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10554-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35459923 Free PMC article.
-
Baicalein-corrected gut microbiota may underlie the amelioration of memory and cognitive deficits in APP/PS1 mice.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 30;14:1132857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1132857. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37063260 Free PMC article.
-
Gut Fungi in Alzheimer's Disease: Mechanisms, Biomarkers and Therapeutic Potential.Aging Dis. 2025 May 14. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.1310. Online ahead of print. Aging Dis. 2025. PMID: 40423640 Review.
-
Herbal medicines in Alzheimer's disease and the involvement of gut microbiota.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 16;15:1416502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1416502. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39081953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The potential of the gut microbiome for identifying Alzheimer's disease diagnostic biomarkers and future therapies.Front Neurosci. 2023 Apr 27;17:1130730. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1130730. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37179559 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosomal MicroRNAs modulate the cognitive function in fasudil treated APPswe/PSEN1dE9 transgenic (APP/PS1) mice model of Alzheimer's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2024 Oct;39(7):1335-1351. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01395-8. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2024. PMID: 39088109 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Based Biomarkers for Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis and Progression: An Overview.Cells. 2022 Apr 17;11(8):1367. doi: 10.3390/cells11081367. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocol for a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind phase IIa study of the safety, tolerability, and symptomatic efficacy of the ROCK-inhibitor Fasudil in patients with Parkinson's disease (ROCK-PD).Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 Feb 14;16:1308577. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1308577. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38419648 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of fasudil treatment in the APPswe/PSEN1dE9 transgenic (APP/PS1) mice model of Alzheimer's disease.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 22;12(1):6625. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-10554-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35459923 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beydoun M. A., Beydoun H. A., Weiss J., Hossain S., El-Hajj Z. W., Zonderman A. B. (2020). Helicobacter pylori, periodontal pathogens, and their interactive association with incident all-cause and Alzheimer's disease dementia in a large national survey. Mol Psychiatry 10.1038/s41380-020-0736-2. [Epub ahead of print]. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

