Computed Tomography Image under Convolutional Neural Network Deep Learning Algorithm in Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Lung Function Examination
- PMID: 34721823
- PMCID: PMC8556120
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3417285
Computed Tomography Image under Convolutional Neural Network Deep Learning Algorithm in Pulmonary Nodule Detection and Lung Function Examination
Abstract
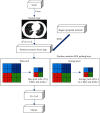
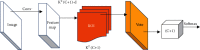
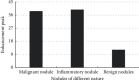
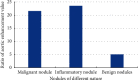
The objective of this study was to perform segmentation and extraction of CT images of pulmonary nodules based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). The Mask-RCNN algorithm model is a typical end-to-end image segmentation model, which uses the R-FCN structure for nodule detection. The effect of applying the two algorithm models to the computed tomography (CT) diagnosis of pulmonary nodules was analyzed, and different indexes of pulmonary nodule CT images in lung function examination after algorithm optimization were compared. A total of 56 patients diagnosed with pulmonary nodules by surgery or puncture were taken as the research objects. Based on the Mask-RCNN algorithm, a model for CT image segmentation processing of pulmonary nodules was proposed. Subsequently, the 3D Faster-RCNN model was used to label the nodules in the pulmonary nodules. The experimental results showed that the trained Mask-RCNN algorithm model can effectively complete the segmentation task of lung CT images, but there was a little jitter at the boundary. The speed of R-FCN algorithm for nodular detection was 0.172 seconds/picture, and the accuracy was 88.9%. CT scans were performed on the 56 patients based on a deep learning algorithm. The results showed that 30 cases of malignant pulmonary nodules were confirmed, and the diagnostic accuracy was 93.75%. There were 22 benign lesions, the diagnostic accuracy was 91.67%, and the overall diagnostic accuracy was 92.85%. This study effectively improved the diagnostic efficiency of CT images of pulmonary nodules, and the accuracy of CT images in the diagnosis of pulmonary nodules was analyzed and evaluated. It provided theoretical support for the follow-up diagnosis of pulmonary nodules and the treatment of lung cancer. It also significantly improved the diagnostic effect and detection efficiency of pulmonary nodules.
Copyright © 2021 Chan Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Construction of U-Net++ pulmonary nodule intelligent analysis model based on feature weighted aggregation.Technol Health Care. 2023;31(S1):477-486. doi: 10.3233/THC-236041. Technol Health Care. 2023. PMID: 37066943 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and fully-automated detection and segmentation of pulmonary nodules in thoracic CT scans using deep convolutional neural networks.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2019 Jun;74:25-36. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Mar 22. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2019. PMID: 30954678
-
Fully automatic deep learning-based lung parenchyma segmentation and boundary correction in thoracic CT scans.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024 Feb;19(2):261-272. doi: 10.1007/s11548-023-03010-0. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2024. PMID: 37594684
-
Deep neural network pulmonary nodule segmentation methods for CT images: Literature review and experimental comparisons.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Sep;164:107321. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.107321. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37595518 Review.
-
Deep learning-based CAD schemes for the detection and classification of lung nodules from CT images: A survey.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(4):591-617. doi: 10.3233/XST-200660. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32568165 Review.
Cited by
-
Deep Learning-Based Chest CT Image Features in Diagnosis of Lung Cancer.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jan 19;2022:4153211. doi: 10.1155/2022/4153211. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Nov 1;2023:9817864. doi: 10.1155/2023/9817864. PMID: 35096129 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
A systematic review on deep learning-based automated cancer diagnosis models.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Mar;28(6):e18144. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18144. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38426930 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

