Neuroprotective Effects of Estradiol plus Lithium Chloride via Anti-Apoptosis and Neurogenesis Pathway in In Vitro and In Vivo Parkinson's Disease Models
- PMID: 34721835
- PMCID: PMC8556090
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3064892
Neuroprotective Effects of Estradiol plus Lithium Chloride via Anti-Apoptosis and Neurogenesis Pathway in In Vitro and In Vivo Parkinson's Disease Models
Abstract
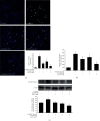
Few pharmaceutical agents for slowing Parkinson's disease (PD) progression existed, especially for perimenopause females. The current general medications are mostly hormone replacement therapy and may have some side effects. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a novel treatment for PD. This study examined the possibility of estradiol plus lithium chloride (LiCl), one of the metal halides used as an alternative to salt. We showed that the combination of LiCl and estradiol could enhance neurogenesis proteins GAP-43 and N-myc in the human neuronal-like cells. We also further confirmed the neurogenesis activity in zebrafish. LiCl and LiCl plus estradiol could enhance 6-OHDA-induced upregulation of TGase-2b and Rho A mRNA expression. Besides, LiCl plus estradiol showed a synergic effect in anti-apoptotic activity. LiCl plus estradiol protected SH-SY5Y cells and zebrafish against 6-OHDA-induced damage on neurons than LiCl or estradiol alone groups via p-P38, p-Akt, Bcl-2, and caspase-3 cascade. The potential for developing this combination as a candidate treatment for PD is discussed.
Copyright © 2021 Yung-Shih Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
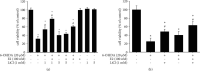






Similar articles
-
Salidroside Protection Against Oxidative Stress Injury Through the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Rats with Parkinson's Disease.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(5):1793-1806. doi: 10.1159/000489365. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. Retraction in: Cell Physiol Biochem. 2021;55(5):670. doi: 10.33594/000000460. PMID: 29705802 Retracted.
-
Evaluation of the neuroprotective potential of caffeic acid phenethyl ester in a cellular model of Parkinson's disease.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 15;883:173342. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173342. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32634439
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Stellettin B Through Anti-Apoptosis and the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway.Mar Drugs. 2019 May 29;17(6):315. doi: 10.3390/md17060315. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31146323 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-410 exerts neuroprotective effects in a cellular model of Parkinson's disease induced by 6-hydroxydopamine via inhibiting the PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Aug;109:16-24. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 5. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31067440
-
Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3β by lithium chloride suppresses 6-hydroxydopamine-induced inflammatory response in primary cultured astrocytes.Neurochem Int. 2013 Nov;63(5):345-53. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.07.003. Epub 2013 Jul 16. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23871716
Cited by
-
Prenatal lipopolysaccharide exposure induces anxiety-like behaviour in male mouse offspring and aberrant glial differentiation of embryonic neural stem cells.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Aug 17;28(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00480-7. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37592237 Free PMC article.
-
The Neuroprotective Effect of Isotetrandrine on Parkinson's Disease via Anti-Inflammation and Antiapoptosis In Vitro and In Vivo.Parkinsons Dis. 2023 Oct 10;2023:8444153. doi: 10.1155/2023/8444153. eCollection 2023. Parkinsons Dis. 2023. PMID: 37854894 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

