Prenatal diagnosis of Pfeiffer syndrome type 2 with increased nuchal translucency
- PMID: 34721862
- PMCID: PMC8543055
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.5001
Prenatal diagnosis of Pfeiffer syndrome type 2 with increased nuchal translucency
Abstract
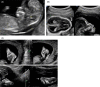
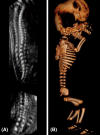
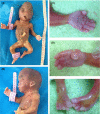
Pfeiffer syndrome (PS) is a rare autosomal dominant genetic disorder characterized by craniosynostosis, broad thumbs / toes. Here, we report a case of PS type 2 with increased nuchal translucency in early trimester.
Keywords: Pfeiffer syndrome; increased nuchal translucency; prenatal diagnosis.
© 2021 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no any conflict of interest in relation to the work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pfeiffer Syndrome Type 3 and Prune Belly Anomaly in a Female: Case Report and Review.Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2019 Oct;38(5):412-417. doi: 10.1080/15513815.2019.1603256. Epub 2019 Apr 19. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31002276
-
A case of Pfeiffer syndrome with c833_834GC>TG (Cys278Leu) mutation in the FGFR2 gene.Korean J Pediatr. 2010 Jul;53(7):774-7. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2010.53.7.774. Epub 2010 Jul 31. Korean J Pediatr. 2010. PMID: 21189955 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal diagnosis of Pfeiffer syndrome type II.Prenat Diagn. 2004 Aug;24(8):644-6. doi: 10.1002/pd.960. Prenat Diagn. 2004. PMID: 15305355
-
Pfeiffer syndrome: literature review of prenatal sonographic findings and genetic diagnosis.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017 Sep;30(18):2225-2231. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2016.1243099. Epub 2016 Oct 20. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017. PMID: 27762162 Review.
-
Pfeiffer syndrome: systemic and ocular implications.Optometry. 2005 Jul;76(7):352-62. doi: 10.1016/j.optm.2005.05.002. Optometry. 2005. PMID: 16038862 Review.
Cited by
-
A Rare Case of Prenatally Diagnosed Pfeiffer Syndrome with Multicystic Kidney.J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2025 Apr;75(Suppl 1):610-612. doi: 10.1007/s13224-024-02020-5. Epub 2024 Sep 14. J Obstet Gynaecol India. 2025. PMID: 40390968
References
-
- Cohen MM Jr. Pfeiffer syndrome update, clinical subtypes, and guidelines for differential diagnosis. Am J Med Genet. 1993;45(3):300‐307. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein PS, Gross SJ, Cohen DJ, et al. Prenatal diagnosis of type 2 Pfeiffer syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 1996;8(6):425‐428. - PubMed
-
- Syngelaki A, Hammami A, Bower S, et al. Diagnosis of fetal non‐chromosomal abnormalities on routine ultrasound examination at 11–13 weeks’ gestation. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2019;54(4):468‐476. - PubMed
-
- Dall'Asta A, Paramasivam G, Lees C, et al. The brain shadowing sign: A clue finding for early suspicion of craniosynostosis? Fetal Diagn Ther. 2019;45(5):357‐360. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

