Weighted butterfly optimization algorithm with intuitionistic fuzzy Gaussian function based adaptive-neuro fuzzy inference system for covid-19 prediction
- PMID: 34722166
- PMCID: PMC8542441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.10.153
Weighted butterfly optimization algorithm with intuitionistic fuzzy Gaussian function based adaptive-neuro fuzzy inference system for covid-19 prediction
Abstract
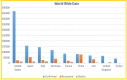
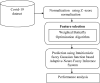
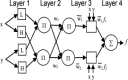
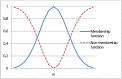
Covid-19 cases are increasing each day, however none of the countries successfully came up with a proper approved vaccine. Studies suggest that the virus enters the body causing a respiratory infection post contact with a disease. Measures like screening and early diagnosis contribute towards the management of COVID- 19 thereby reducing the load of health care systems. Recent studies have provided promising methods that will be applicable for the current pandemic situation. The previous system designed a various Machine Learning (ML) algorithms such as Decision Tree (DT), Random Forest (RF), XGBoost, Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) and Support Vector Machine (SVM) for predicting COVID-19 disease with symptoms. However, it does not produce satisfactory results in terms of true positive rate. And also, better optimization methods are required to enhance the precision rate with minimum execution time. To solve this problem the proposed system designed a Weighted Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (WBOA) with Intuitionistic fuzzy Gaussian function based Adaptive-Neuro Fuzzy Inference System (IFGF-ANFIS) classifier for predicting the magnitude of COVID- 19 disease. The principle aim of this method is to design an algorithm that could predict and assess the COVID-19 parameters. Initially, the dataset regarding COVID-19 is taken as an input and preprocessed. The parameters included are age, sex, history of fever, travel history, presence of cough and lung infection. Then the optimal features are selected by using Weighted Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (WBOA) to improve the classification accuracy. Based on the selected features, an Intuitionistic fuzzy Gaussian function based Adaptive-Neuro Fuzzy Inference System (IFGF-ANFIS) classifier is utilized for classifying the people having infection possibility. The studies conducted on this proposed system indicates that it is capable of producing better results than the other systems especially in terms of accuracy, precision, recall and f-measure.
Keywords: Adaptive-Neuro Fuzzy Inference System (IFGF-(ANFIS); Classification accuracy; Covid-19 prediction; Intuitionistic fuzzy Gaussian function; Weighted Butterfly Optimization Algorithm (WBOA).
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Selection and peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the First International Conference on Design and Materials (ICDM)-2021.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
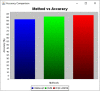
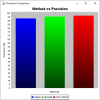
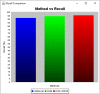
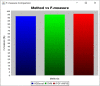
References
-
- Alazab M., Awajan A., Mesleh A., Abraham A., Jatana V., Alhyari S. COVID-19 prediction and detection using deep learning. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. Ind. Manage. Appl. 2020;12:168–181.
-
- Saumendra Kumar Mohapatra, Mohan Debarchan Mohanty, Mihir Narayan Mohanty Corona virus infection probability classification using support vector machine. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Technol. 2020;29(8s):3093–3098.
-
- Jewell C.P., Kypraios T., Christley R.M., Roberts G.O. A novel approach to real-time risk prediction for emerging infectious diseases: a case study in Avian Influenza H5N1. Prev. Veter. Med. 2009;91(1):19–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
