SNHG8 Promotes the Progression of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer via Sponging miR-512-5p and Targeting TRIM28
- PMID: 34722282
- PMCID: PMC8554152
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.734694
SNHG8 Promotes the Progression of Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Gastric Cancer via Sponging miR-512-5p and Targeting TRIM28
Abstract
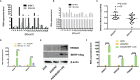
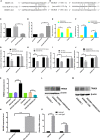
SNHG8, a family member of small nucleolar RNA host genes (SNHG), has been reported to act as an oncogene in gastric carcinoma (GC). However, its biological function in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-associated gastric cancer (EBVaGC) remains unclear. This study investigated the role of SNHG8 in EBVaGC. Sixty-one cases of EBVaGC, 20 cases of non-EBV-infected gastric cancer (EBVnGC), and relative cell lines were studied for the expression of SNHG8 and BHRF1 (BCL2 homolog reading frame 1) encoded by EBV with Western blot and qRT-PCR assays. The relationship between the expression levels of SNHG8 and the clinical outcome in 61 EBVaGC cases was analyzed. Effects of overexpression or knockdown of BHRF1, SNHG8, or TRIM28 on cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle and the related molecules were determined by several assays, including cell proliferation, colony assay, wound healing assay, transwell invasion assay, cell circle with flow cytometry, qRT-PCR, and Western blot for expression levels. The interactions among SNHG8, miR-512-5p, and TRIM28 were determined with Luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP), pull-down assays, and Western blot assay. The in vivo activity of SNHG8 was assessed with SNHG8 knockdown tumor xenografts in zebrafish. Results demonstrated that the following. (1) BHRF1 and SNHG8 were overexpressed in EBV-encoded RNA 1-positive EBVaGC tissues and cell lines. BHRF1 upregulated the expressions of SNHG8 and TRIM28 in AGS. (2) SNHG8 overexpression had a significant correlation with tumor size and vascular tumor thrombus. Patients with high SNHG8 expression had poorer overall survival (OS) compared to those with low SNHG8 expression. (3) SNHG8 overexpression promoted EBVaGC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and in vivo, cell cycle arrested at the G2/M phase via the activation of BCL-2, CCND1, PCNA, PARP1, CDH1, CDH2 VIM, and Snail. (4) Results of dual-luciferase reporter assay, RNA immunoprecipitation, and pull-down assays indicated that SNHG8 sponged miR-512-5p, which targeted on TRIM28 and promoted cancer malignant behaviors of EBVaGC cells. Our data suggest that BHRF1 triggered the expression of SNHG8, which sponged miR-512-5p and upregulated TRIM28 and a set of effectors (such as BCL-2, CCND1, CDH1, CDH2 Snail, and VIM) to promote EBVaGC tumorigenesis and invasion. SNHG8 could be an independent prognostic factor for EBVaGC and sever as target for EBVaGC therapy.
Keywords: EBVaGC; SNHG8; TRIM28; cell proliferation; invasion; miR-512-5p; migration.
Copyright © 2021 Zou, Liao, Hu, Su, Lin, Lin, Luo, Zheng, Zhang, Huang and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
SNHG8 is identified as a key regulator in non-small-cell lung cancer progression sponging to miR-542-3p by targeting CCND1/CDK6.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Sep 20;11:6081-6090. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S170482. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 30275712 Free PMC article.
-
lncRNA SNHG8 Promotes the Tumorigenesis and Metastasis by Sponging miR-149-5p and Predicts Tumor Recurrence in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(5):2262-2274. doi: 10.1159/000495871. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30537734
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART11-3p modulates the DUSP6-MAPK axis to promote gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis.J Virol. 2023 Sep 28;97(9):e0088123. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00881-23. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 37681959 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the role of SNHG8 in human disorders.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 May;245:154458. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154458. Epub 2023 Apr 7. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 37043963 Review.
-
The role of EBV-encoded miRNA in EBV-associated gastric cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 14;13:1204030. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1204030. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37388232 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SNHG8 and its role in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric cancer: Is NF-κB involved?Cancer Pathog Ther. 2023 Mar 13;1(3):224-226. doi: 10.1016/j.cpt.2023.03.001. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cancer Pathog Ther. 2023. PMID: 38327835 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
TRIM28 Regulates Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells Partly Through SRF/IDO1 Axis.J Cancer. 2024 Jun 11;15(13):4417-4429. doi: 10.7150/jca.95094. eCollection 2024. J Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38947391 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM28 in cancer and cancer therapy.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 19;15:1431564. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1431564. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39100077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of tripartite motif-containing 28 in cancer progression and its therapeutic potentials.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 23;13:1100134. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1100134. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36756159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The viral etiology of EBV-associated gastric cancers contributes to their unique pathology, clinical outcomes, treatment responses and immune landscape.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1358511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1358511. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596668 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

