miRNA-204-5p acts as tumor suppressor to influence the invasion and migration of astrocytoma by targeting ezrin and is downregulated by DNA methylation
- PMID: 34723710
- PMCID: PMC8809991
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2000244
miRNA-204-5p acts as tumor suppressor to influence the invasion and migration of astrocytoma by targeting ezrin and is downregulated by DNA methylation
Abstract
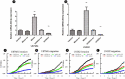
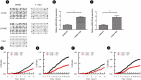
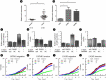
microRNAs (miRNAs), through their regulation of the expression and activity of numerous proteins, are involved in almost all cellular processes. As a consequence, dysregulation of miRNA expression is closely associated with the development and progression of cancers. Recently, DNA methylation has been shown to play a key role in miRNA expression dysregulation in tumors. miRNA-204-5p commonly acts in the suppression of oncogenes in tumors. In this study, the levels of miRNA-204-5p were found to be down-regulated in the astrocytoma samples. miRNA-204-5p expression was also down-regulated in two astrocytoma cell lines (U87MG and LN382). Examination of online databases showed that the miRNA-204-5p promoter regions exist in CpG islands, which might be subjected to differential methylation. Subsequently, we showed that the miRNA-204-5p promoter region was hypermethylated in the astrocytoma tissue samples and cell lines. Then we found that ezrin expression was down-regulated with an increase in miRNA-204-5p expression in LN382 and U87MG cells after 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5'AZA) treatment compared with control DMSO treatment. In addition, LN382 and U87MG cells treated with 5'AZA exhibited significantly inhibited cell invasion and migration . In a recovery experiment, cell invasion and migration returned to normal levels as miRNA-204-5p and ezrin levels were restored. Overall, our study suggests that miRNA-204-5p acts as a tumor suppressor to influence astrocytoma invasion and migration by targeting ezrin and that miRNA-204-5p expression is downregulated by DNA methylation. This study provides a new potential strategy for astrocytoma treatment.
Keywords: DNA methylation; astrocytoma; ezrin; invasion and migration; miRNA-204-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Shuangshoti S, Thorner PS, Ruangvejvorachai P, et al. J1-31 protein expression in astrocytes and astrocytomas. Neuropathology. 2009. Oct;29(5):521–527. - PubMed
-
- Gabayan AJ, Green SB, Sanan A, et al. GliaSite brachytherapy for treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis. Neurosurgery. 2006Apr; 582: 701–709. discussion 701-709 - PubMed
-
- Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, et al. Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2014. Feb 20;370(8):709–722. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
