Lung Microenvironments and Disease Progression in Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- PMID: 34724391
- PMCID: PMC8865586
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.202103-0569OC
Lung Microenvironments and Disease Progression in Fibrotic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
Abstract
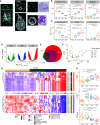
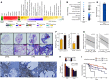
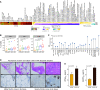
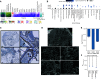
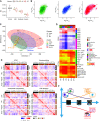
Rationale: Fibrotic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (fHP) is an interstitial lung disease caused by sensitization to an inhaled allergen. Objectives: To identify the molecular determinants associated with progression of fibrosis. Methods: Nine fHP explant lungs and six unused donor lungs (as controls) were systematically sampled (4 samples/lung). According to microcomputed tomography measures, fHP cores were clustered into mild, moderate, and severe fibrosis groups. Gene expression profiles were assessed using weighted gene co-expression network analysis, xCell, gene ontology, and structure enrichment analysis. Gene expression of the prevailing molecular traits was also compared with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The explant lung findings were evaluated in separate clinical fHP cohorts using tissue, BAL samples, and computed tomography scans. Measurements and Main Results: We found six molecular traits that associated with differential lung involvement. In fHP, extracellular matrix and antigen presentation/sensitization transcriptomic signatures characterized lung zones with only mild structural and histological changes, whereas signatures involved in honeycombing and B cells dominated the transcriptome in the most severely affected lung zones. With increasing disease severity, endothelial function was progressively lost, and progressive disruption in normal cellular homeostatic processes emerged. All six were also found in IPF, with largely similar associations with disease microenvironments. The molecular traits correlated with in vivo disease behavior in a separate clinical fHP cohort. Conclusions: We identified six molecular traits that characterize the morphological progression of fHP and associate with in vivo clinical behavior. Comparing IPF with fHP, the transcriptome landscape was determined considerably by local disease extent rather than by diagnosis alone.
Keywords: extrinsic allergic alveolitis; pulmonary fibrosis; transcriptome.
Figures



Comment in
-
Cut from the Same Cloth: Similarities between Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022 Jan 1;205(1):4-6. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2211ED. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022. PMID: 34748715 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Solaymani-Dodaran M, West J, Smith C, Hubbard R. Extrinsic allergic alveolitis: incidence and mortality in the general population. QJM . 2007;100:233–237. - PubMed
-
- Nance S, Cross R, Yi AK, Fitzpatrick EA. IFN-γ production by innate immune cells is sufficient for development of hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Eur J Immunol . 2005;35:1928–1938. - PubMed
-
- Barrera L, Mendoza F, Zuñiga J, Estrada A, Zamora AC, Melendro EI, et al. Functional diversity of T-cell subpopulations in subacute and chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2008;177:44–55. - PubMed
-
- Vasakova M, Selman M, Morell F, Sterclova M, Molina-Molina M, Raghu G. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis: current concepts of pathogenesis and potential targets for treatment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med . 2019;200:rccm.201903-0541PP. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

