Myeloid-Specific Deficiency of Long-Chain Acyl CoA Synthetase 4 Reduces Inflammation by Remodeling Phospholipids and Reducing Production of Arachidonic Acid-Derived Proinflammatory Lipid Mediators
- PMID: 34725110
- PMCID: PMC8802997
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100393
Myeloid-Specific Deficiency of Long-Chain Acyl CoA Synthetase 4 Reduces Inflammation by Remodeling Phospholipids and Reducing Production of Arachidonic Acid-Derived Proinflammatory Lipid Mediators
Erratum in
-
Correction: Myeloid-Specific Deficiency of Long-Chain Acyl CoA Synthetase 4 Reduces Inflammation by Remodeling Phospholipids and Reducing Production of Arachidonic Acid-Derived Proinflammatory Lipid Mediators.J Immunol. 2022 Jun 1;208(11):2593. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200133. Epub 2022 May 16. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35577369 No abstract available.
Abstract
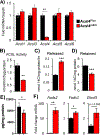
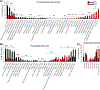
In response to infection or tissue damage, resident peritoneal macrophages (rpMACs) produce inflammatory lipid mediators from the polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA), arachidonic acid (AA). Long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase 4 (ACSL4) catalyzes the covalent addition of a CoA moiety to fatty acids, with a strong preference for AA and other PUFAs containing three or more double bonds. PUFA-CoA can be incorporated into phospholipids, which is the source of PUFA for lipid mediator synthesis. In this study, we demonstrated that deficiency of Acsl4 in mouse rpMACs resulted in a significant reduction of AA incorporated into all phospholipid classes and a reciprocal increase in incorporation of oleic acid and linoleic acid. After stimulation with opsonized zymosan (opZym), a diverse array of AA-derived lipid mediators, including leukotrienes, PGs, hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, and lipoxins, were produced and were significantly reduced in Acsl4-deficient rpMACs. The Acsl4-deficient rpMACs stimulated with opZym also demonstrated an acute reduction in mRNA expression of the inflammatory cytokines, Il6, Ccl2, Nos2, and Ccl5 When Acsl4-deficient rpMACs were incubated in vitro with the TLR4 agonist, LPS, the levels of leukotriene B4 and PGE2 were also significantly decreased. In LPS-induced peritonitis, mice with myeloid-specific Acsl4 deficiency had a significant reduction in leukotriene B4 and PGE2 levels in peritoneal exudates, which was coupled with reduced infiltration of neutrophils in the peritoneal cavity as compared with wild-type mice. Our data demonstrate that chronic deficiency of Acsl4 in rpMACs reduces the incorporation of AA into phospholipids, which reduces lipid mediator synthesis and inflammation.
Copyright © 2021 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures
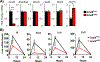
References
-
- Wang J, and Kubes P. 2016. A Reservoir of Mature Cavity Macrophages that Can Rapidly Invade Visceral Organs to Affect Tissue Repair. Cell 165: 668–678. - PubMed
-
- Ajuebor MN, Das AM, Virág L, Flower RJ, Szabó C, and Perretti M. 1999. Role of Resident Peritoneal Macrophages and Mast Cells in Chemokine Production and Neutrophil Migration in Acute Inflammation: Evidence for an Inhibitory Loop Involving Endogenous IL-10. The Journal of Immunology 162: 1685–1691. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

