Sentinels of chromatin: chromodomain helicase DNA-binding proteins in development and disease
- PMID: 34725129
- PMCID: PMC8559672
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.348897.121
Sentinels of chromatin: chromodomain helicase DNA-binding proteins in development and disease
Abstract
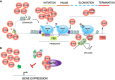
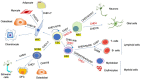
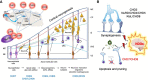
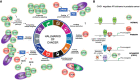
Chromatin is highly dynamic, undergoing continuous global changes in its structure and type of histone and DNA modifications governed by processes such as transcription, repair, replication, and recombination. Members of the chromodomain helicase DNA-binding (CHD) family of enzymes are ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers that are intimately involved in the regulation of chromatin dynamics, altering nucleosomal structure and DNA accessibility. Genetic studies in yeast, fruit flies, zebrafish, and mice underscore essential roles of CHD enzymes in regulating cellular fate and identity, as well as proper embryonic development. With the advent of next-generation sequencing, evidence is emerging that these enzymes are subjected to frequent DNA copy number alterations or mutations and show aberrant expression in malignancies and other human diseases. As such, they might prove to be valuable biomarkers or targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: cancer; chromatin remodeling; chromodomain helicase DNA-binding proteins; development and disease.
© 2021 Alendar and Berns; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


References
-
- Alendar A, Lambooij J-P, Bhaskaran R, Lancini C, Song J-Y, Vugt Hv, Snoek M, Berns A. 2020. Gene expression regulation by the chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 9 (CHD9) chromatin remodeler is dispensable for murine development. PLoS One 15: e0233394. 10.1371/journal.pone.0233394 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arco PG-D, Perdiguero E, Yunes-Leites PS, Acín-Pérez R, Zeini M, Garcia-Gomez A, Sreenivasan K, Jiménez-Alcázar M, Segalés J, López-Maderuelo D, et al. 2016. The chromatin remodeling complex Chd4/NuRD controls striated muscle identity and metabolic homeostasis. Cell Metab 23: 881–892. 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.04.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
