Anatomical, functional and biomechanical review of the glenoid labrum
- PMID: 34725812
- PMCID: PMC8930820
- DOI: 10.1111/joa.13582
Anatomical, functional and biomechanical review of the glenoid labrum
Abstract
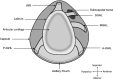
The glenohumeral joint is the most mobile joint in the human skeleton, supported by both active and passive stabilisers. As one of the passive stabilisers, the glenoid labrum has increasingly been recognised to play an important role in stability of the glenohumeral joint, acting to maintain intraarticular pressure, centralise the humeral head and contribute to concavity-compression stability. Several studies have investigated the macro- and micro-anatomical features of the labrum as well as its biomechanical function. However, in order to better understand the role of the labrum and its mechanics, a comprehensive anatomical, functional and biomechanical review of these studies is needed. Therefore, this article reviews the current literature detailing anatomical descriptions of the glenoid labrum, with an emphasis on its function(s) and biomechanics, as well as its interaction with neighbouring structures. The intimate relationship between the labrum and the surrounding structures was found to be important in glenohumeral stability, which owes further investigation into the microanatomy of labrum to better understand this relationship.
Keywords: anatomy; biomechanics; glenohumeral joint; glenohumeral ligaments; glenoid labrum.
© 2021 Anatomical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Alashkham, A. , Alraddadi, A. & Soames, R. (2018) Anatomy of the glenohumeral ligaments. Italian Journal of Anatomy and Embryology, 123, 114–126. 10.13128/IJAE-24160 - DOI
-
- Alashkham, A. , Alraddadi, A. & Soames, R. (2019) Morphometric parameters of the glenoid labrum. European Journal of Anatomy, 23, 41–47.
-
- Barnes, L.F. , Parsons, B.O. , Lippitt, S.B. , Flatow, E.L. & Matsen, F.A.M. III . (2018). Glenohumeral instability. In: Rockwood and Matsen’s The Shoulder. Elsevier Inc, pp. 543–649. 10.1016/B978-0-323-29731-8.00013-1 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

