uPAR: An Essential Factor for Tumor Development
- PMID: 34729105
- PMCID: PMC8558663
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.62281
uPAR: An Essential Factor for Tumor Development
Abstract
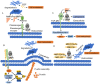
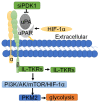
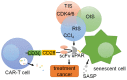
Tumorigenesis is closely related to the loss of control of many genes. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), a glycolipid-anchored protein on the cell surface, is controlled by many factors in tumorigenesis and is expressed in many tumor tissues. In this review, we summarize the regulatory effects of the uPAR signaling pathway on processes and factors related to tumor progression, such as tumor cell proliferation, adhesion, metastasis, glycolysis, tumor microenvironment and angiogenesis. Overall, the evidence accumulated to date suggests that uPAR induction by tumor progression may be one of the most important factors affecting therapeutic efficacy. An improved understanding of the interactions between uPAR and its coreceptors in cancer will provide critical biomolecular information that may help to better predict the disease course and response to therapy.
Keywords: adhesion; cancer therapy; metastasis; proliferation; tumorigenesis; uPAR.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of urokinase receptor in tumor progression and development.Theranostics. 2013 Jun 25;3(7):487-95. doi: 10.7150/thno.4218. Print 2013. Theranostics. 2013. PMID: 23843896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its receptor (uPAR): development of antagonists of uPA/uPAR interaction and their effects in vitro and in vivo.Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9(19):1529-43. doi: 10.2174/1381612033454612. Curr Pharm Des. 2003. PMID: 12871066 Review.
-
The urokinase plasminogen activator system in cancer: implications for tumor angiogenesis and metastasis.Angiogenesis. 1999;3(1):15-32. doi: 10.1023/a:1009095825561. Angiogenesis. 1999. PMID: 14517441
-
Combined overexpression of urokinase, urokinase receptor, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is associated with breast cancer progression: an immunohistochemical comparison of normal, benign, and malignant breast tissues.Cancer. 1996 Mar 15;77(6):1079-88. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0142(19960315)77:6<1079::aid-cncr12>3.0.co;2-z. Cancer. 1996. PMID: 8635127
-
The urokinase receptor promotes cancer metastasis independently of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in mice.Am J Pathol. 2009 Jul;175(1):190-200. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.081053. Epub 2009 Jun 4. Am J Pathol. 2009. PMID: 19497996 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Extensive Review of Nanomedicine Strategies Targeting the Tumor Microenvironment in PDAC.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Mar 17;20:3379-3406. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S504503. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40125427 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulatory effect of metformin and its transporters on immune infiltration in tumor microenvironment: a bioinformatic study with experimental validation.Discov Oncol. 2025 May 31;16(1):973. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02766-y. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40450131 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of cytokines in pleural effusions and corresponding cell lines of small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 31;13(1):5-15. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-569. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38405004 Free PMC article.
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) in Inflammation and Disease: A Unique Inflammatory Pathway Activator.Biomedicines. 2024 May 24;12(6):1167. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061167. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human antibody VH domains targeting uPAR as candidate therapeutics for cancers.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 9;13:1194972. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1194972. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37876962 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith HW, Marshall CJ. Regulation of cell signalling by uPAR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:23–36. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

