The impact of viral mutations on recognition by SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells
- PMID: 34729465
- PMCID: PMC8552693
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103353
The impact of viral mutations on recognition by SARS-CoV-2 specific T cells
Abstract
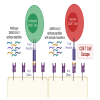
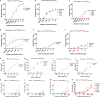
We identify amino acid variants within dominant SARS-CoV-2 T cell epitopes by interrogating global sequence data. Several variants within nucleocapsid and ORF3a epitopes have arisen independently in multiple lineages and result in loss of recognition by epitope-specific T cells assessed by IFN-γ and cytotoxic killing assays. Complete loss of T cell responsiveness was seen due to Q213K in the A∗01:01-restricted CD8+ ORF3a epitope FTSDYYQLY207-215; due to P13L, P13S, and P13T in the B∗27:05-restricted CD8+ nucleocapsid epitope QRNAPRITF9-17; and due to T362I and P365S in the A∗03:01/A∗11:01-restricted CD8+ nucleocapsid epitope KTFPPTEPK361-369. CD8+ T cell lines unable to recognize variant epitopes have diverse T cell receptor repertoires. These data demonstrate the potential for T cell evasion and highlight the need for ongoing surveillance for variants capable of escaping T cell as well as humoral immunity.
Keywords: Immune response; Immunology; Molecular biology; Phylogenetics; Virology.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Agerer B., Koblischke M., Gudipati V., Montano-Gutierrez L.F., Smyth M., Popa A., Genger J.W., Endler L., Florian D.M., Muhlgrabner V., et al. SARS-CoV-2 mutations in MHC-I-restricted epitopes evade CD8(+) T cell responses. Sci. Immunol. 2021;6:eabg6461. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abg6461. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chour W., Xu A.M., Ng A.H.C., Choi J., Xie J., Yuan D., DeLucia D.C., Edmark R.A., Jones L.C., Schmitt T.M., et al. Shared antigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses against the SARS-COV-2 spike protein in HLA-A∗02:01 COVID-19 participants. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.05.04.20085779. - DOI
-
- Ferretti A.P., Kula T., Wang Y., Nguyen D.M.V., Weinheimer A., Dunlap G.S., Xu Q., Nabilsi N., Perullo C.R., Cristofaro A.W., et al. Unbiased screens show CD8(+) T cells of COVID-19 patients recognize shared epitopes in SARS-CoV-2 that largely reside outside the spike protein. Immunity. 2020;53:1095–1107.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goonetilleke N., Liu M.K., Salazar-Gonzalez J.F., Ferrari G., Giorgi E., Ganusov V.V., Keele B.F., Learn G.H., Turnbull E.L., Salazar M.G., et al. The first T cell response to transmitted/founder virus contributes to the control of acute viremia in HIV-1 infection. J. Exp. Med. 2009;206:1253–1272. doi: 10.1084/jem.20090365. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- MC_PC_19012/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204969/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_19025/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R015600/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/V001329/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204911/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 26603/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- MR/P011705/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_19059/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UP_A090_1006/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00008/11/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_19027/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S032304/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/V028448/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L018942/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600520/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001046/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P011705/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

